- Etiology: most commonly due to Wilms tumor / rhabdomyosarcoma / Ewing sarcoma / osteosarcoma, less commonly due to lymphoma / neuroblastoma / synovial cell sarcoma / testicular cancer
- Imaging: usually soft tissue nodule, osteosarcoma metastasis can cause pneumothorax + can be calcified
Radiology Cases of Lung Metastasis
Radiology Cases of Lung Metastasis Due to Wilms Tumor
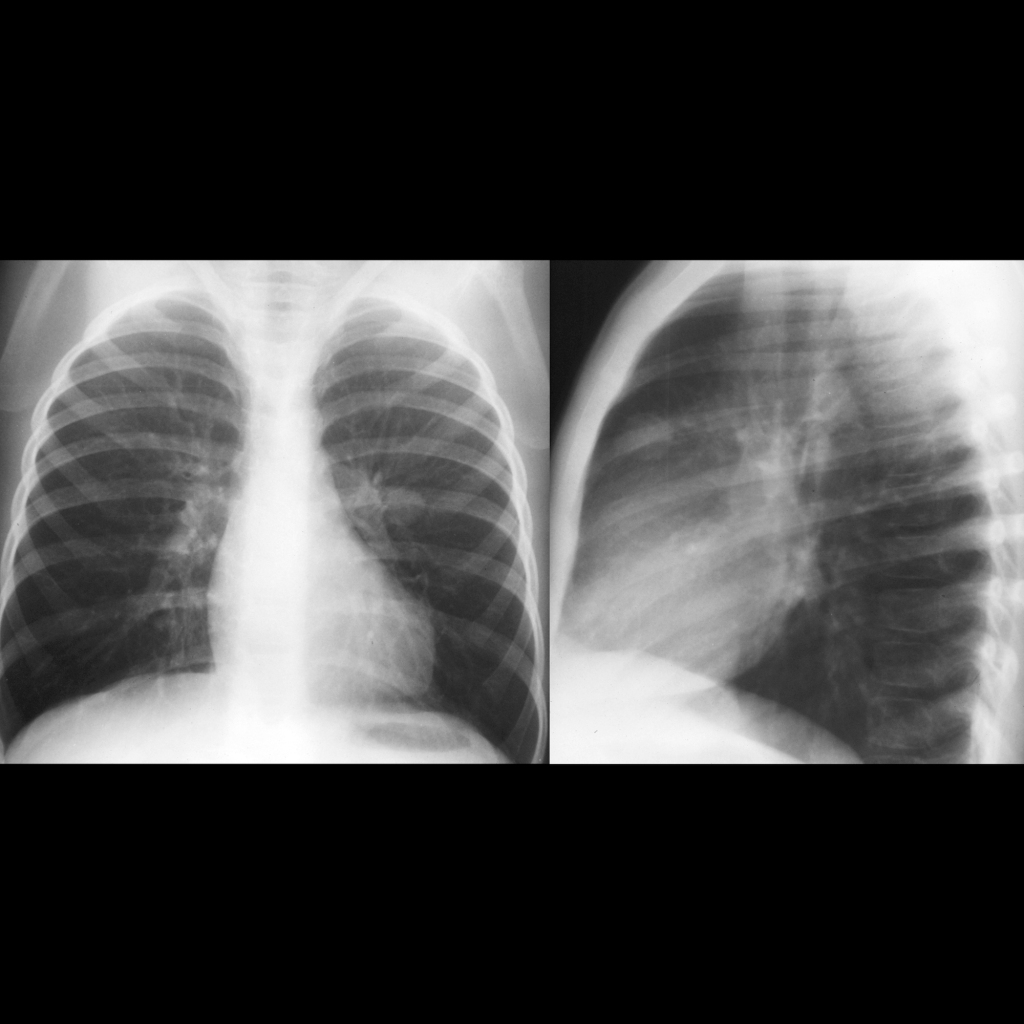
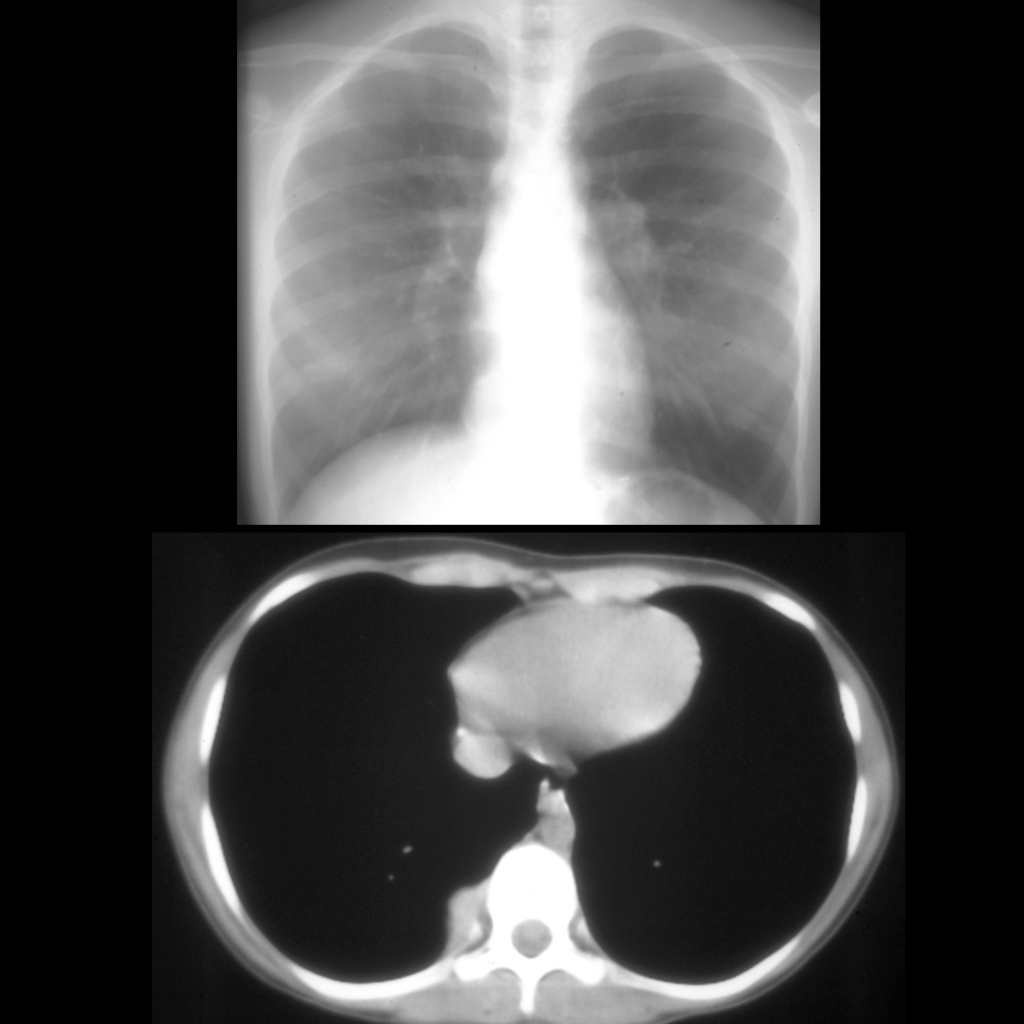
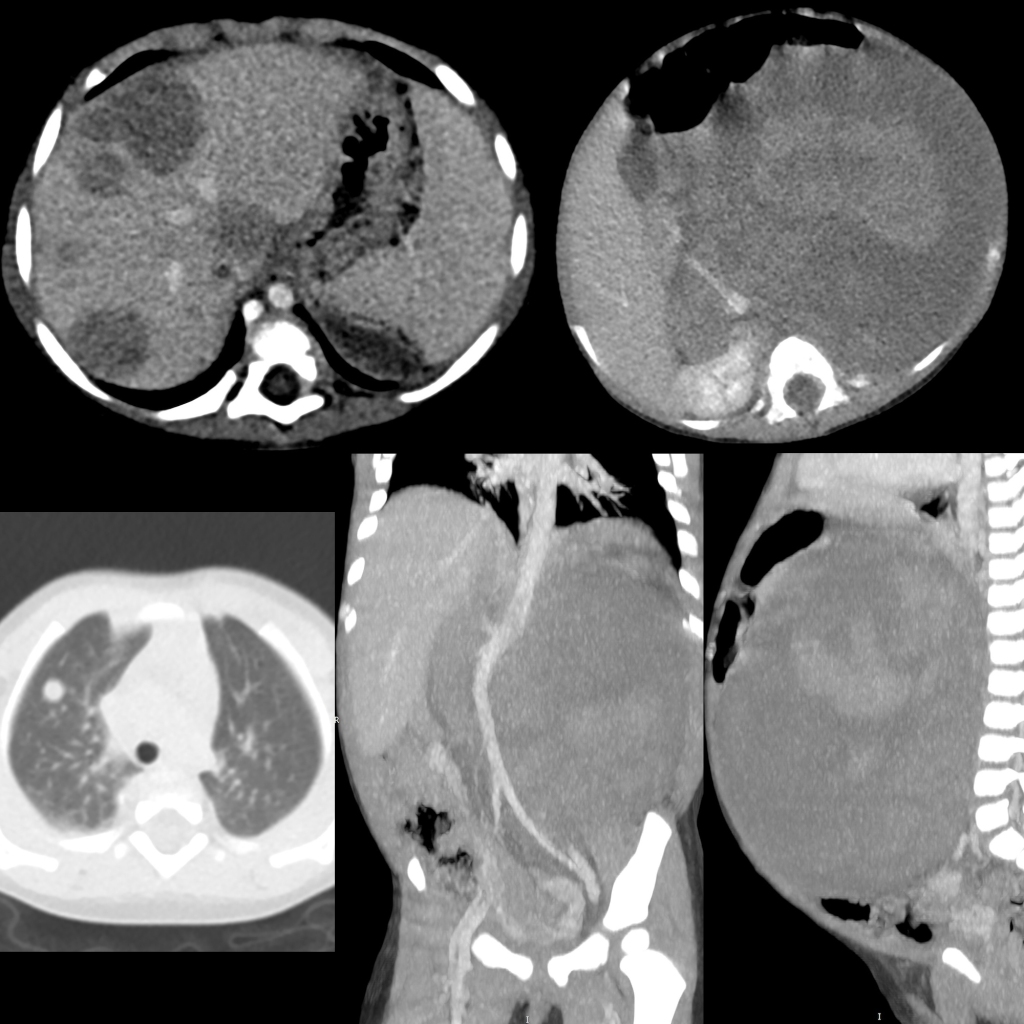
Radiology Cases of Lung Metastasis Due to Testicle Tumor
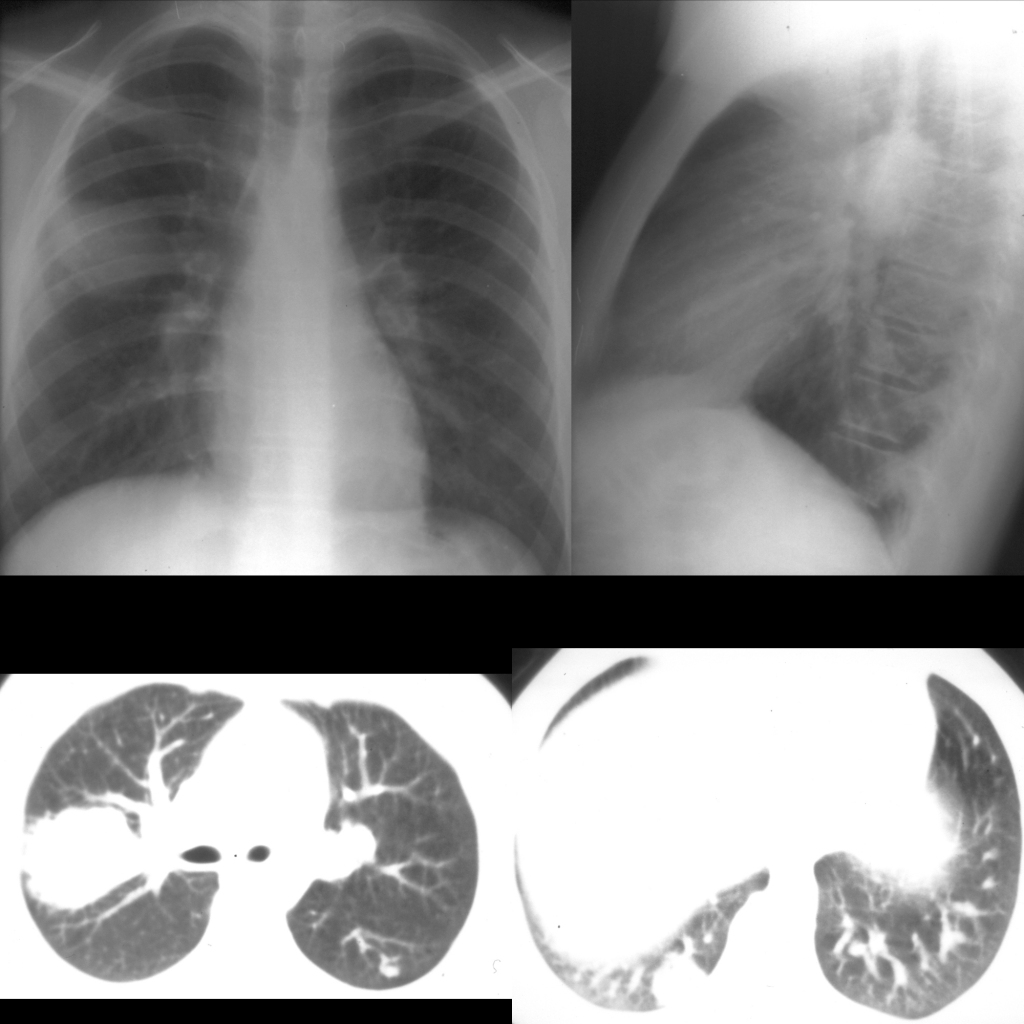
Radiology Cases of Lung Metastases Due to Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma

