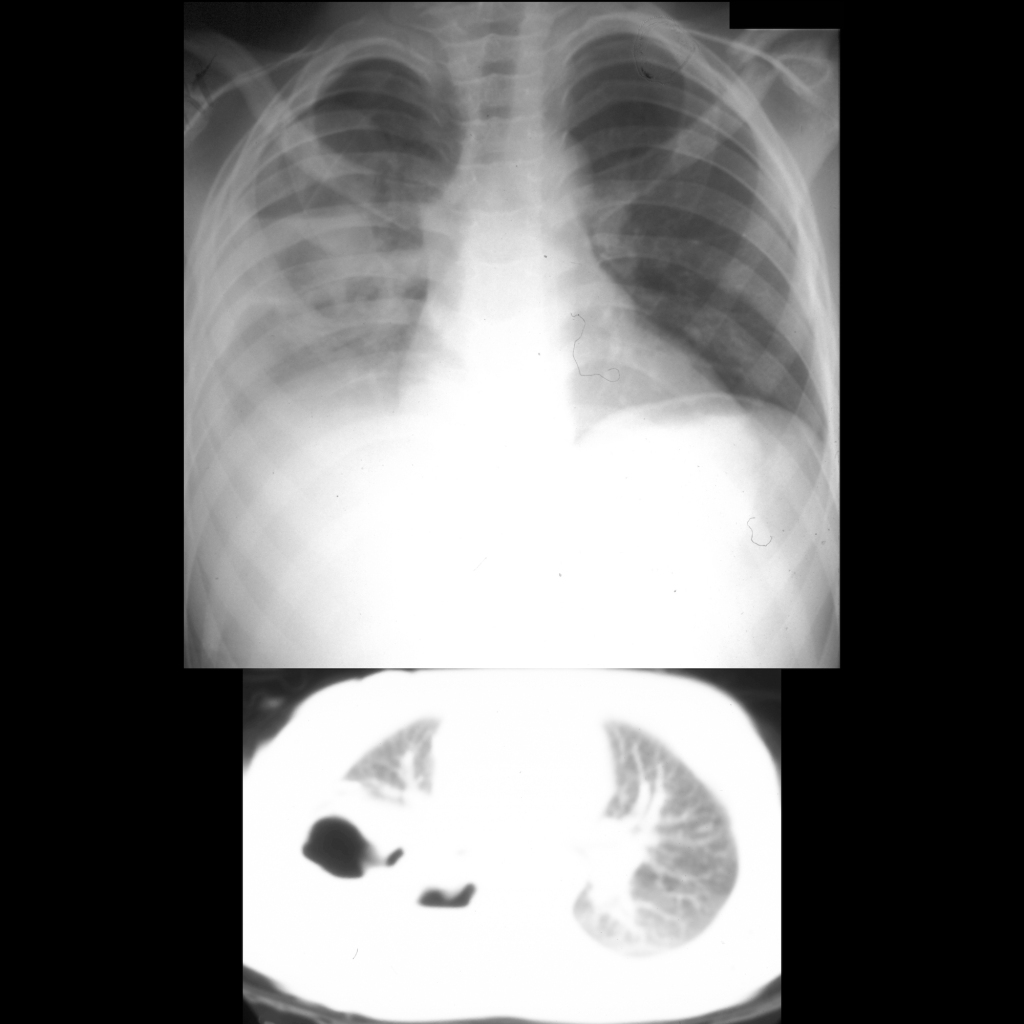
- Etiology: blunt thoracic trauma causes tear in lung parenchyma resulting in cavity that fills with blood
- CXR: often obscured by pulmonary contusion
- CT: round / oval cavity, single or multiple, unilocular or multiloculated
— Air containing = traumatic pneumatocele
— Blood containing = traumatic hematocele
— Air and blood containing = traumatic hematopneumatocele - Clinical: heals slower than pulmonary contusion
Radiology Cases of Pulmonary Laceration