- Etiology: contains endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm tissue and therefore classically can contain fat and calcium
- Layers and what comes from them
— Ectoderm – neural, epidermis
— Mesoderm – bone, muscle, connective tissue, dermis, cardiovascular system, reproductive system, kidneys
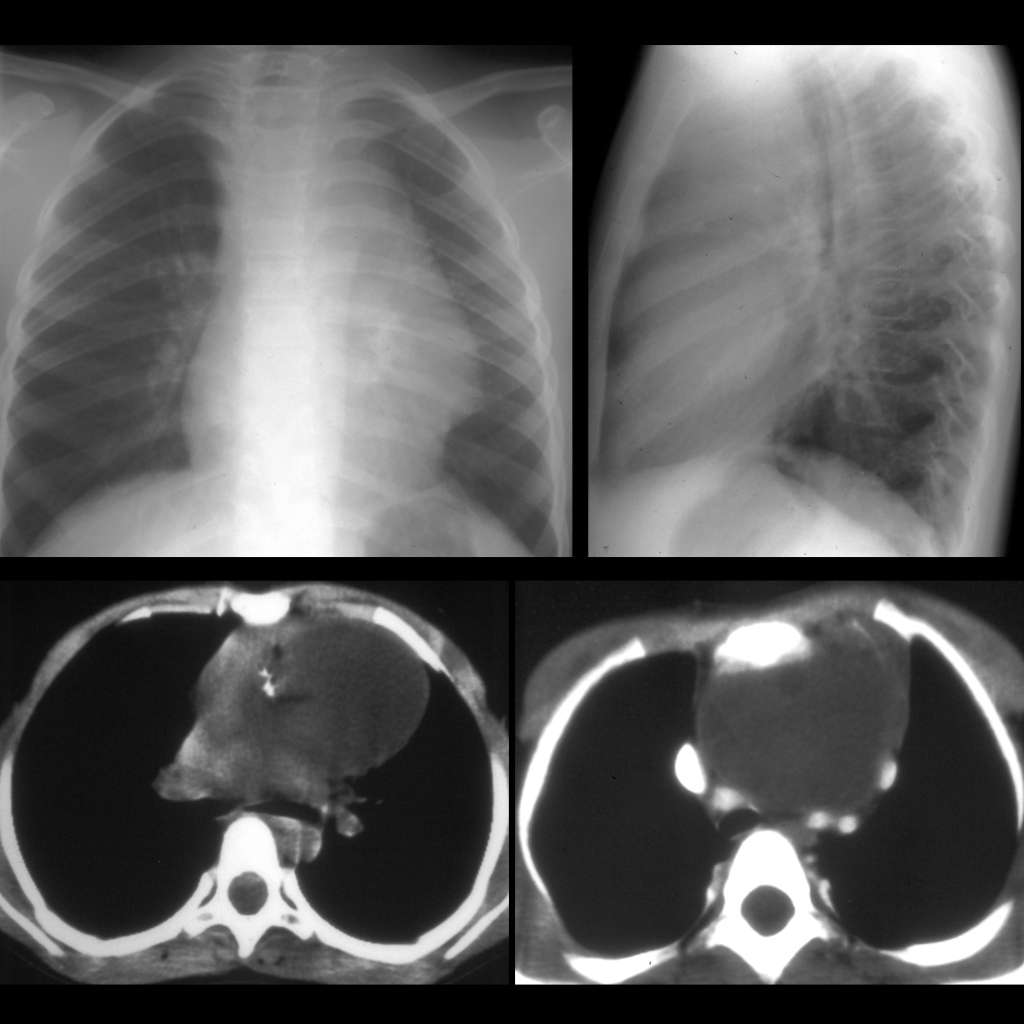
— Endoderm – epithelium gastroinstestinal / respiratory / genitourinary, endocrine glands - Imaging: anterior mediastinal mass arising from thymus which is often heterogenous and may contain fat and calcium
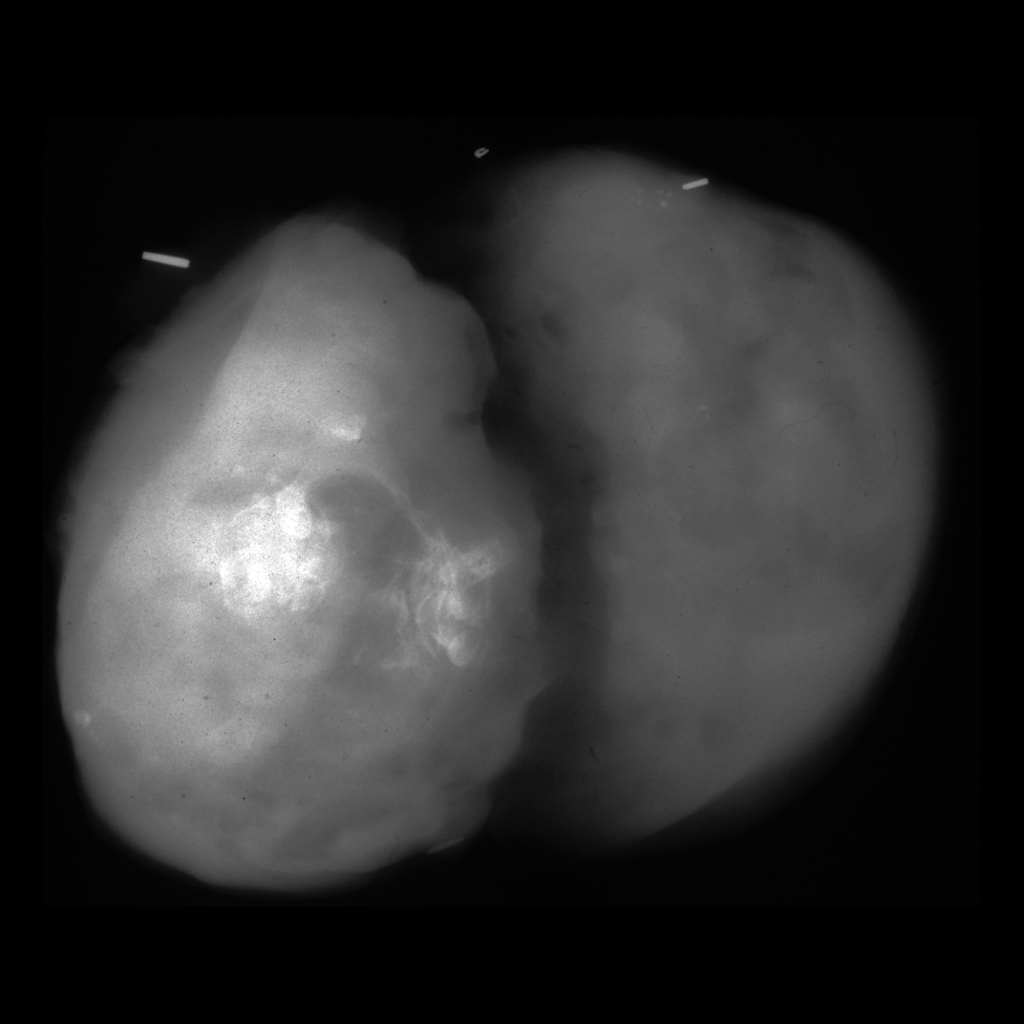
Radiology Cases of Mediastinal Teratoma



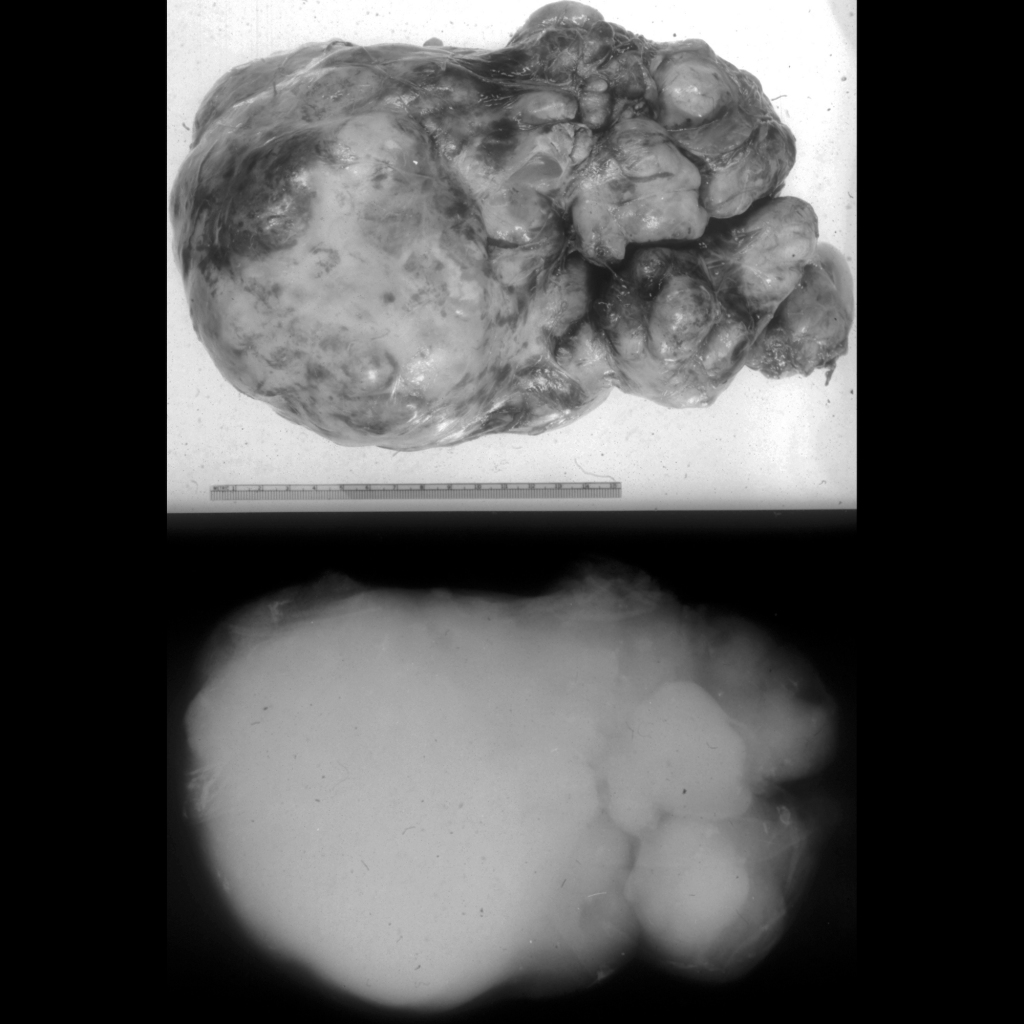
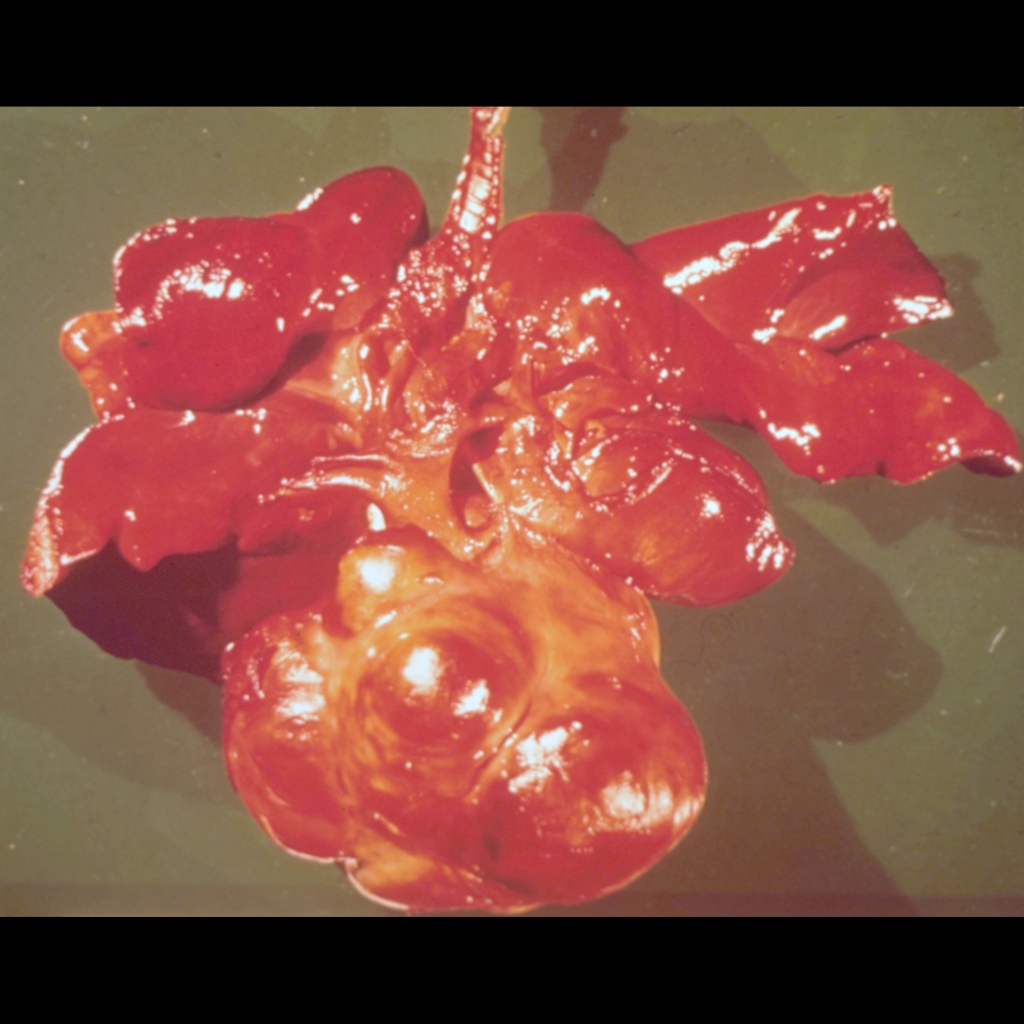
Gross Pathology Cases of Mediastinal Teratoma