
The diagnosis was a simple renal cyst and not a calyceal diverticulum.

The diagnosis was a simple renal cyst and not a calyceal diverticulum.
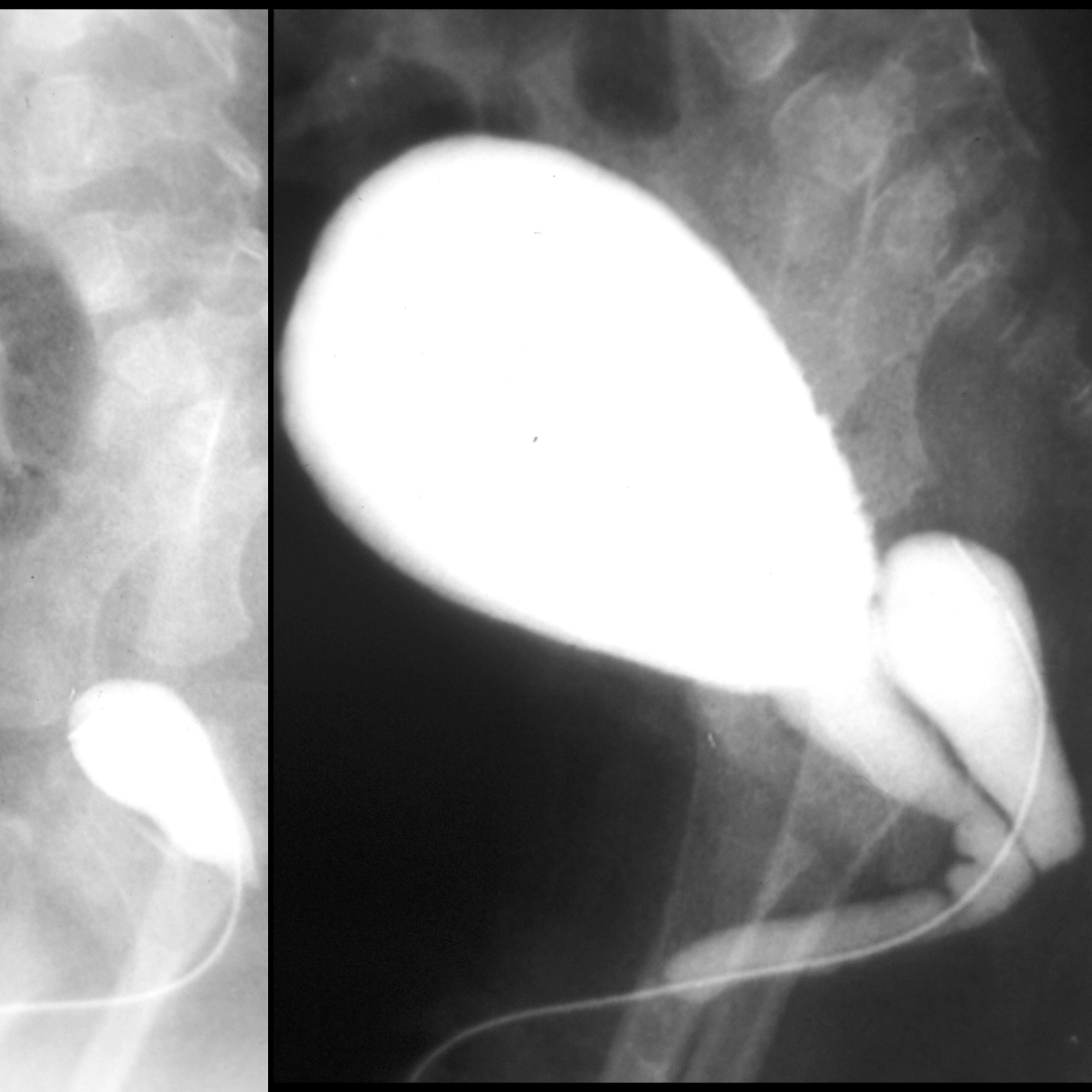
The diagnosis was prostatic utricle cyst.
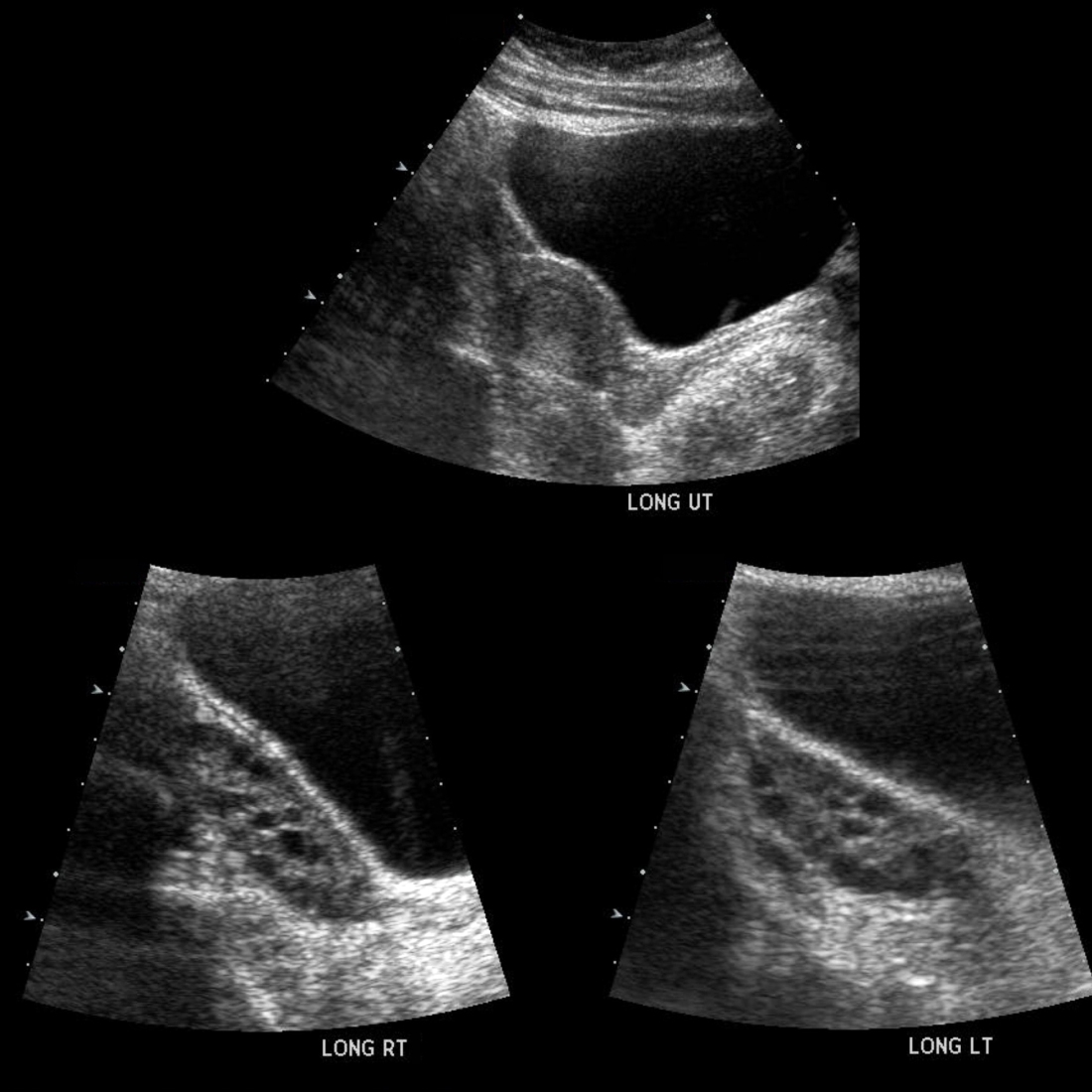
The diagnosis was polycystic ovarian syndrome.
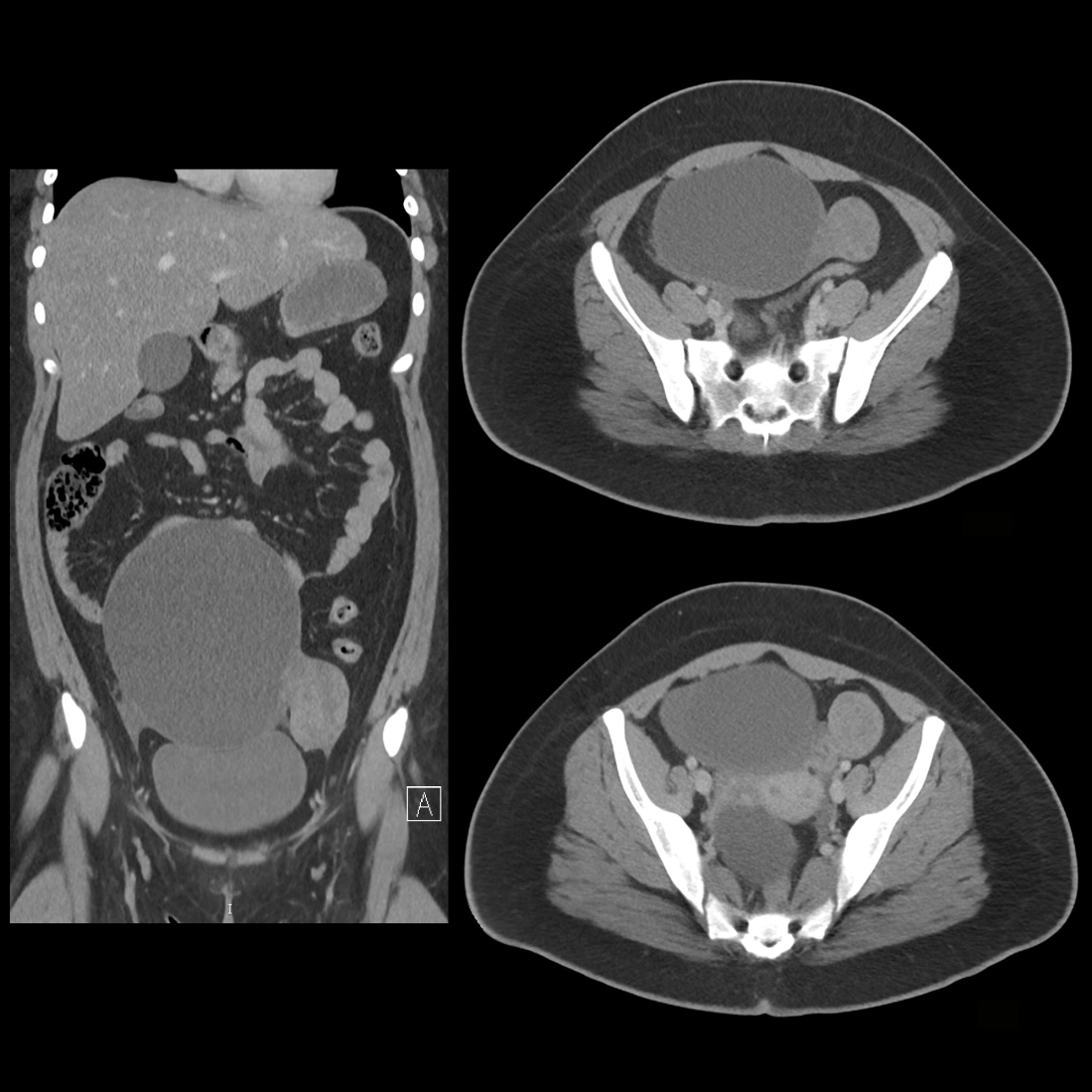
The diagnosis was a large left ovarian cyst and a right paraovarian cyst.
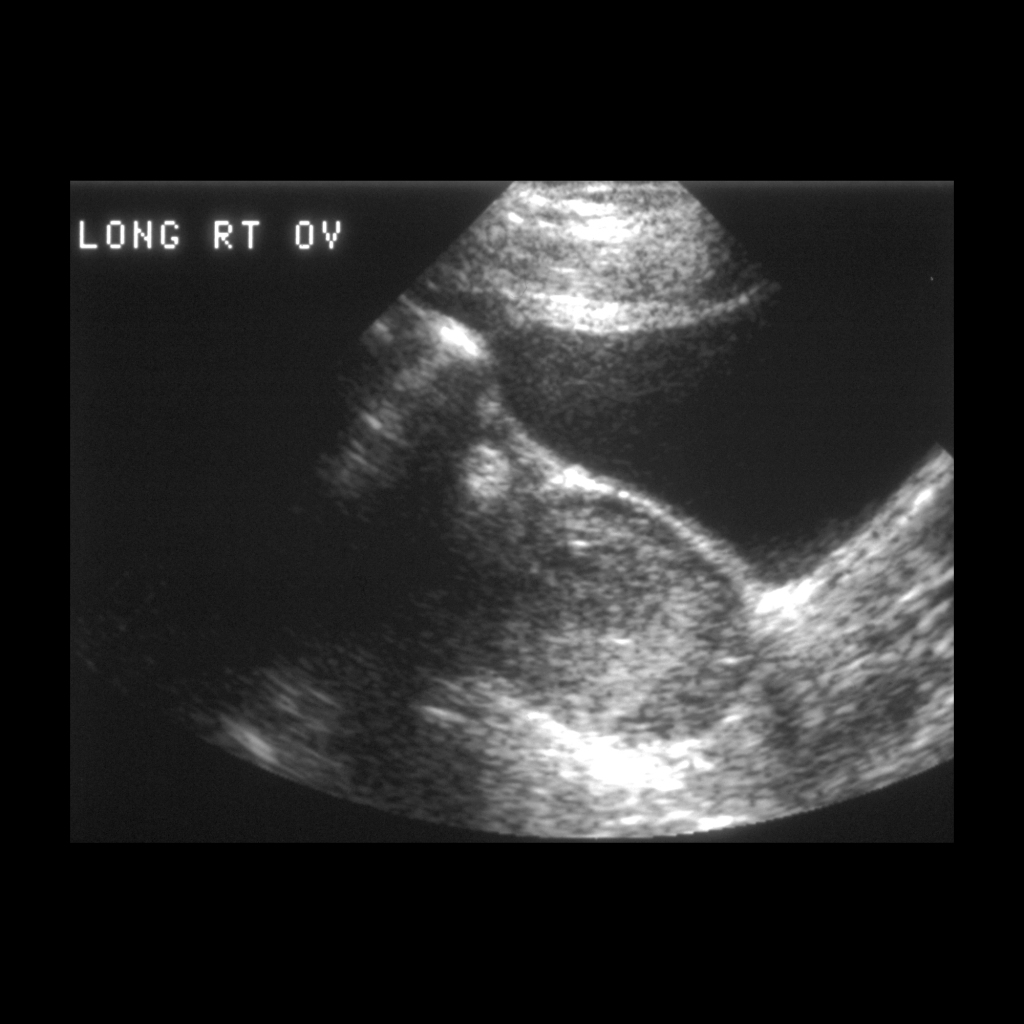
The diagnosis was hemorrhagic ovarian cyst.
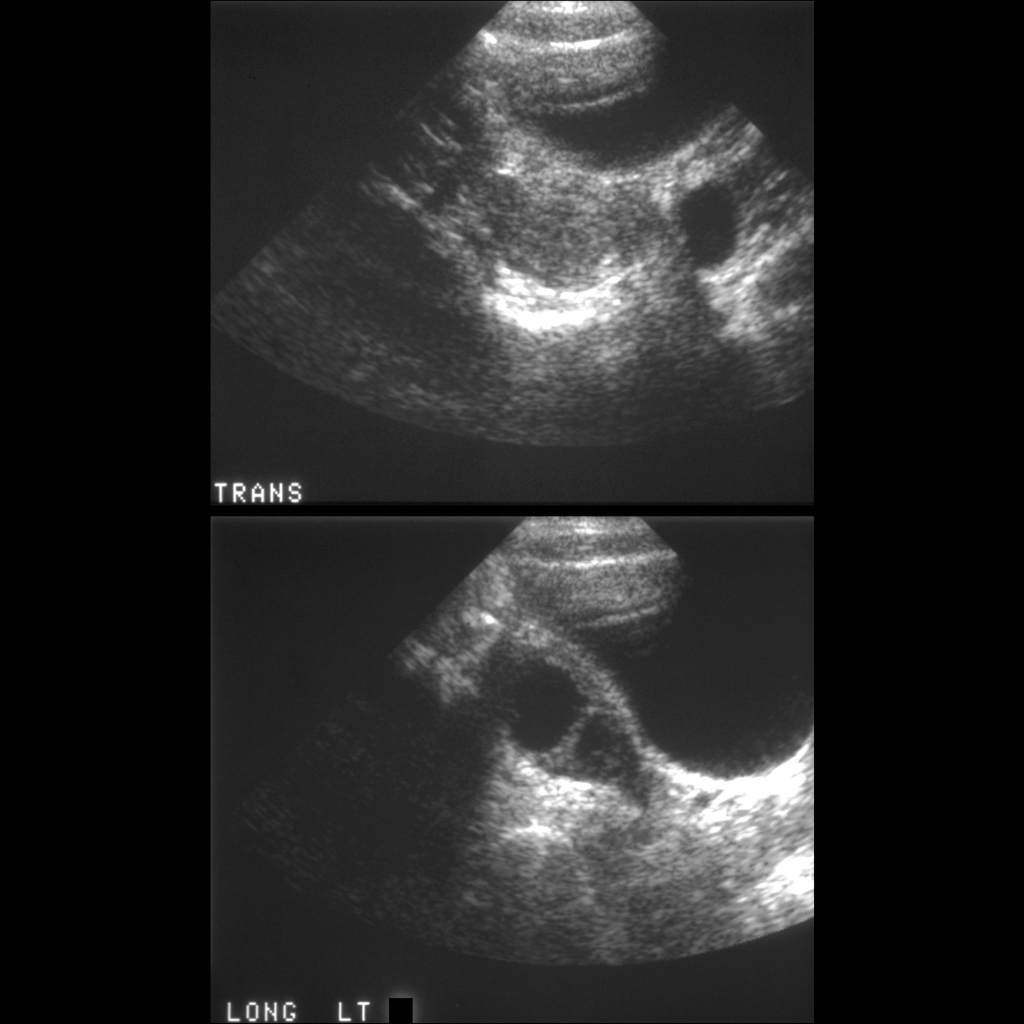
The diagnosis was a simple ovarian cyst.

The diagnosis was a simple ovarian cyst.
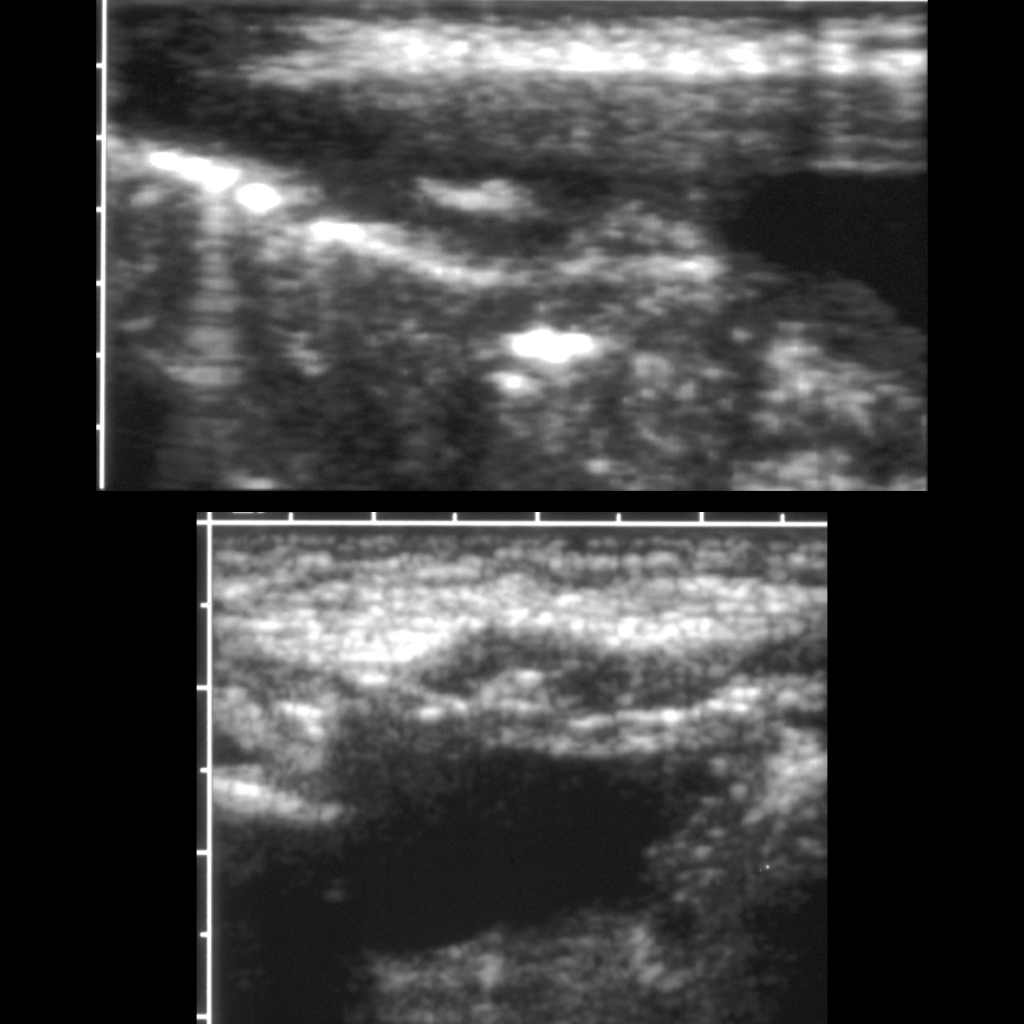
The diagnosis was an infected urachal cyst.
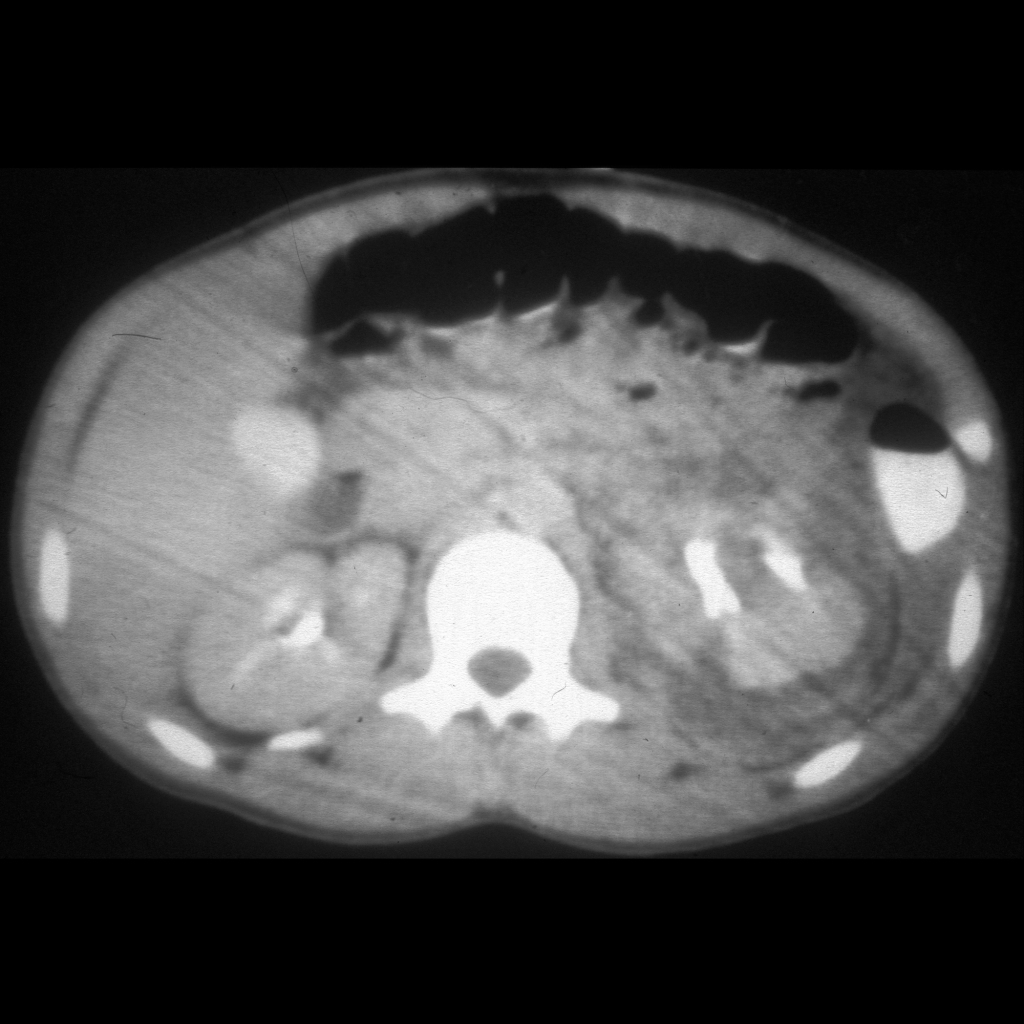
The diagnosis was left renal laceration with perirenal and pararenal hematomas.

The diagnosis was right orchitis.
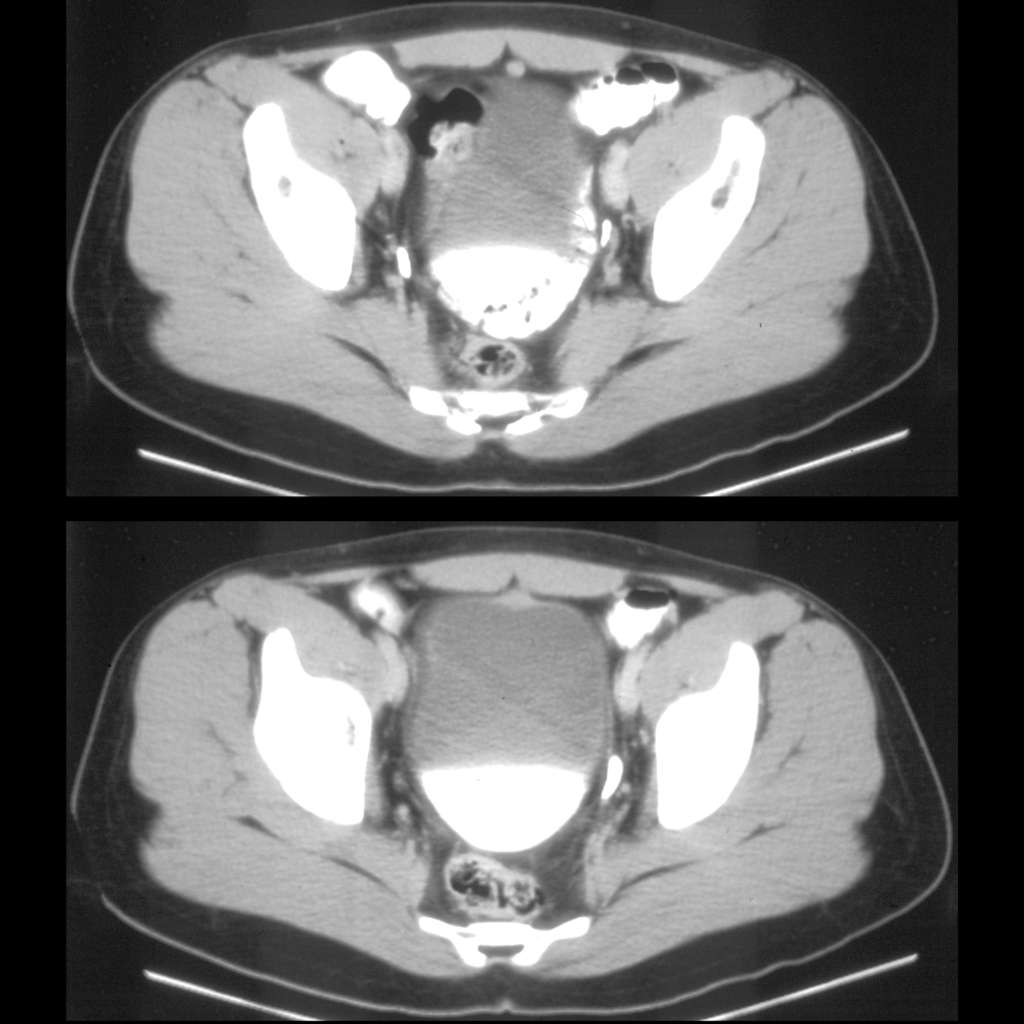
The diagnosis was an obliterated urachal remnant.

The diagnosis was neuroblastoma arising from the left adrenal gland with metastases to the skull.
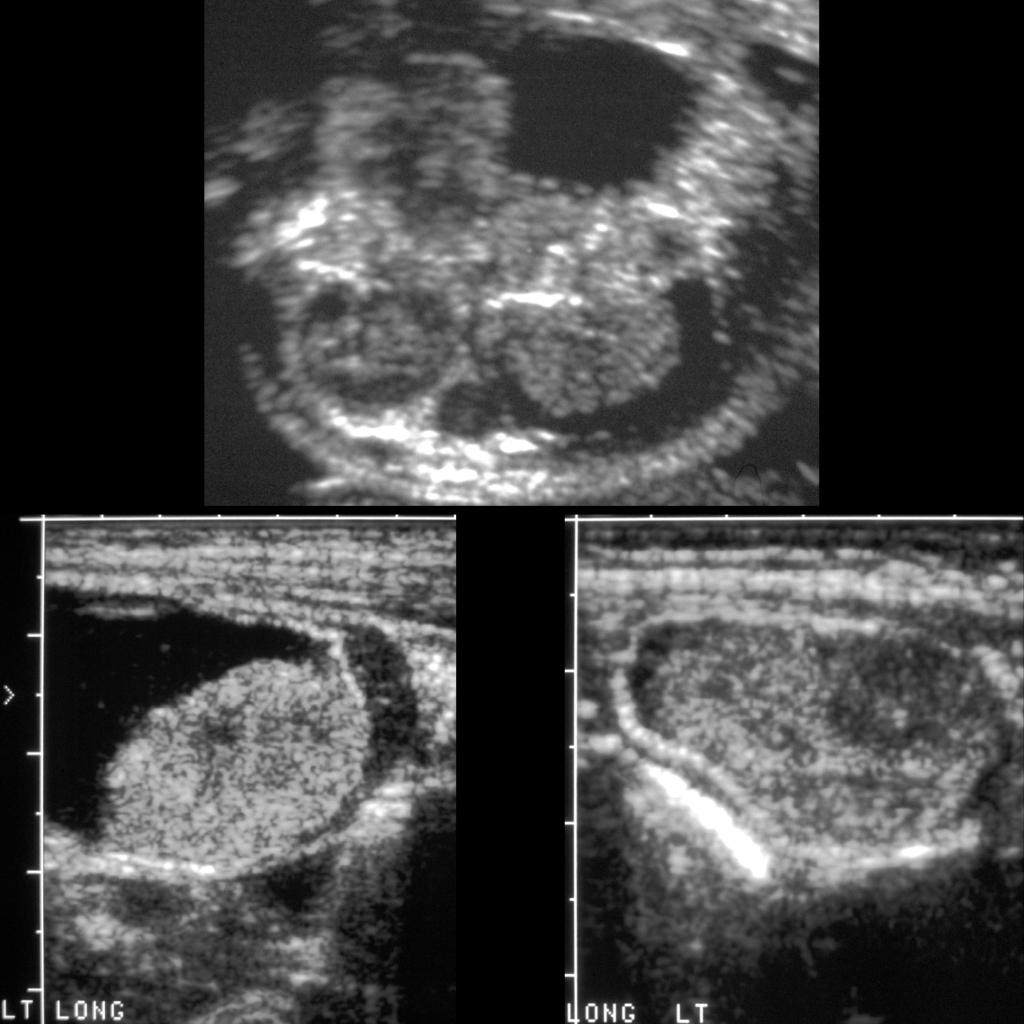
The diagnosis was ovarian torsion of the left ovary due to a neonatal ovarian cyst.
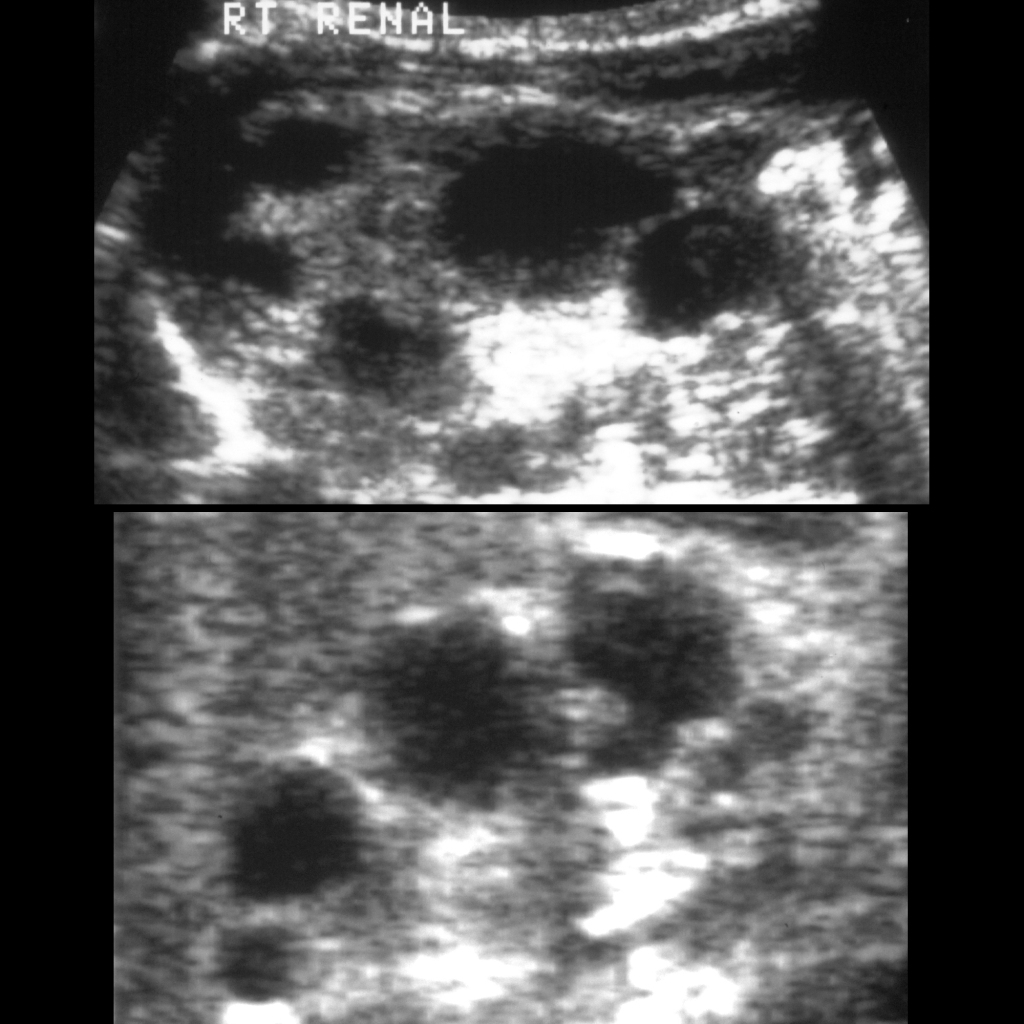
The diagnosis was multicystic dysplastic kidney.
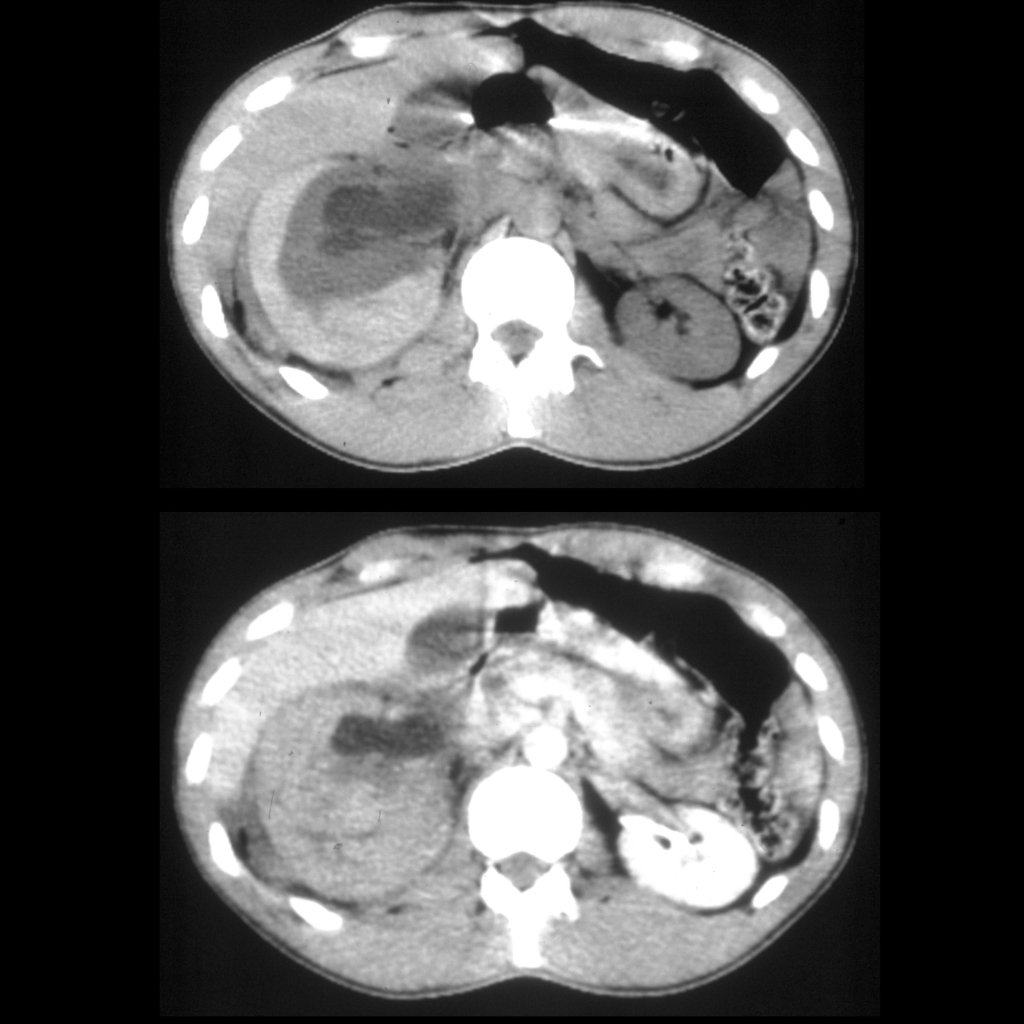
The diagnosis was a right perirenal hematoma in a patient with right ureteropelvic junction obstruction.
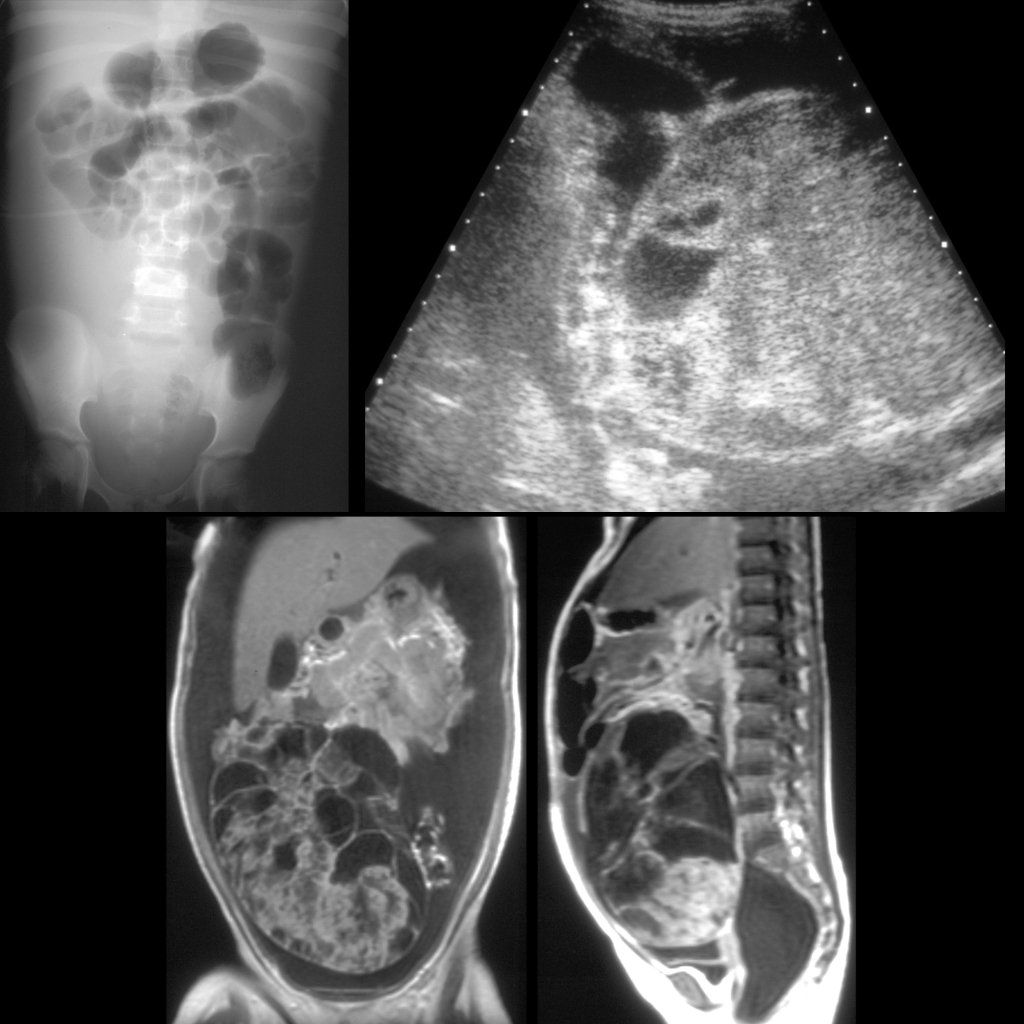
The diagnosis was ovarian endodermal sinus tumor.
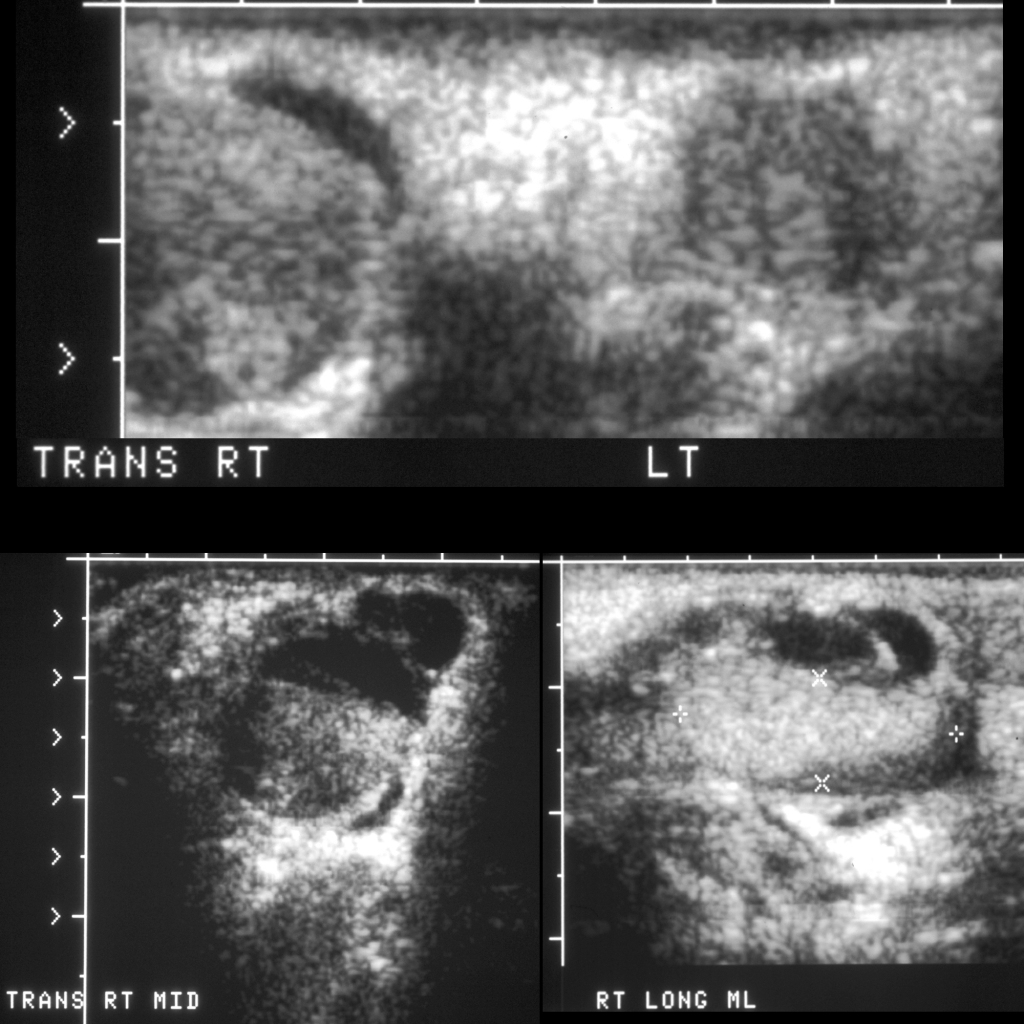
The diagnosis was testicular hematocele.
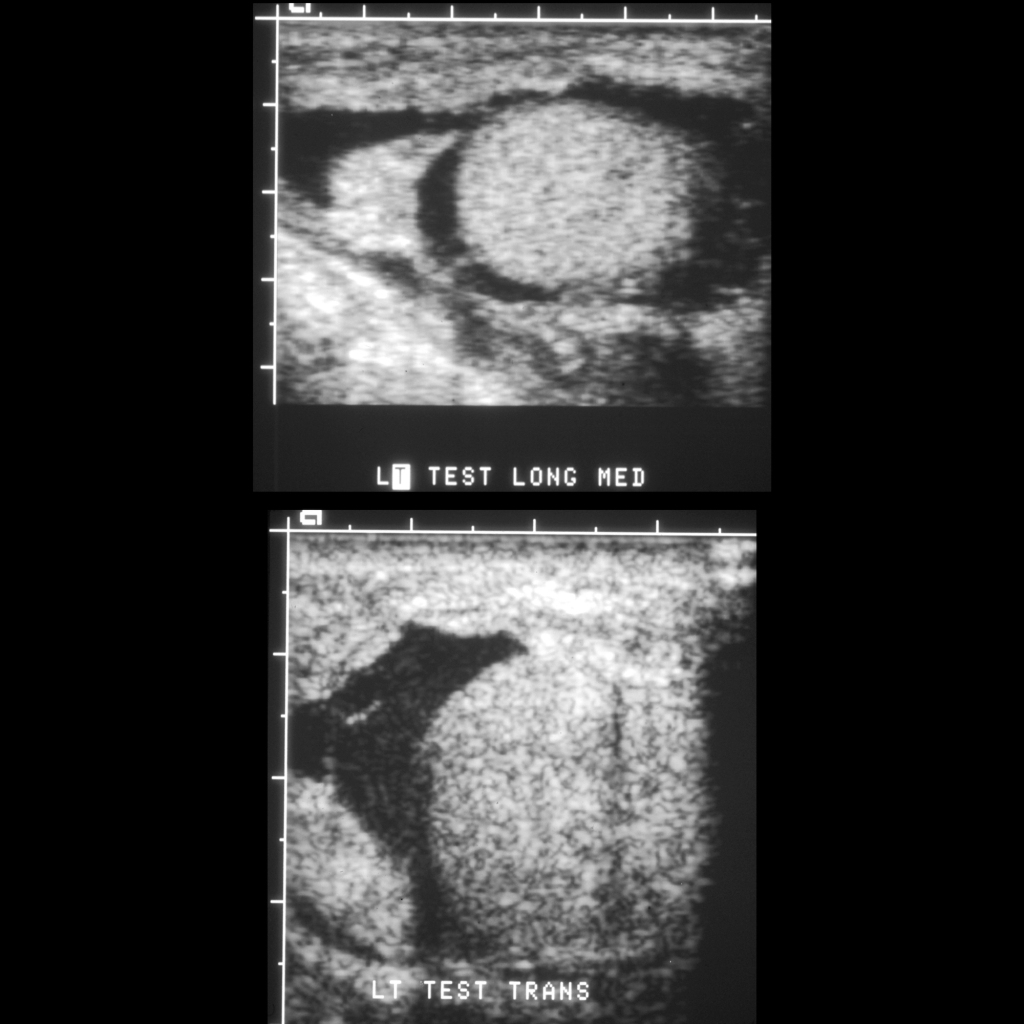
The diagnosis was testicular hematocele.
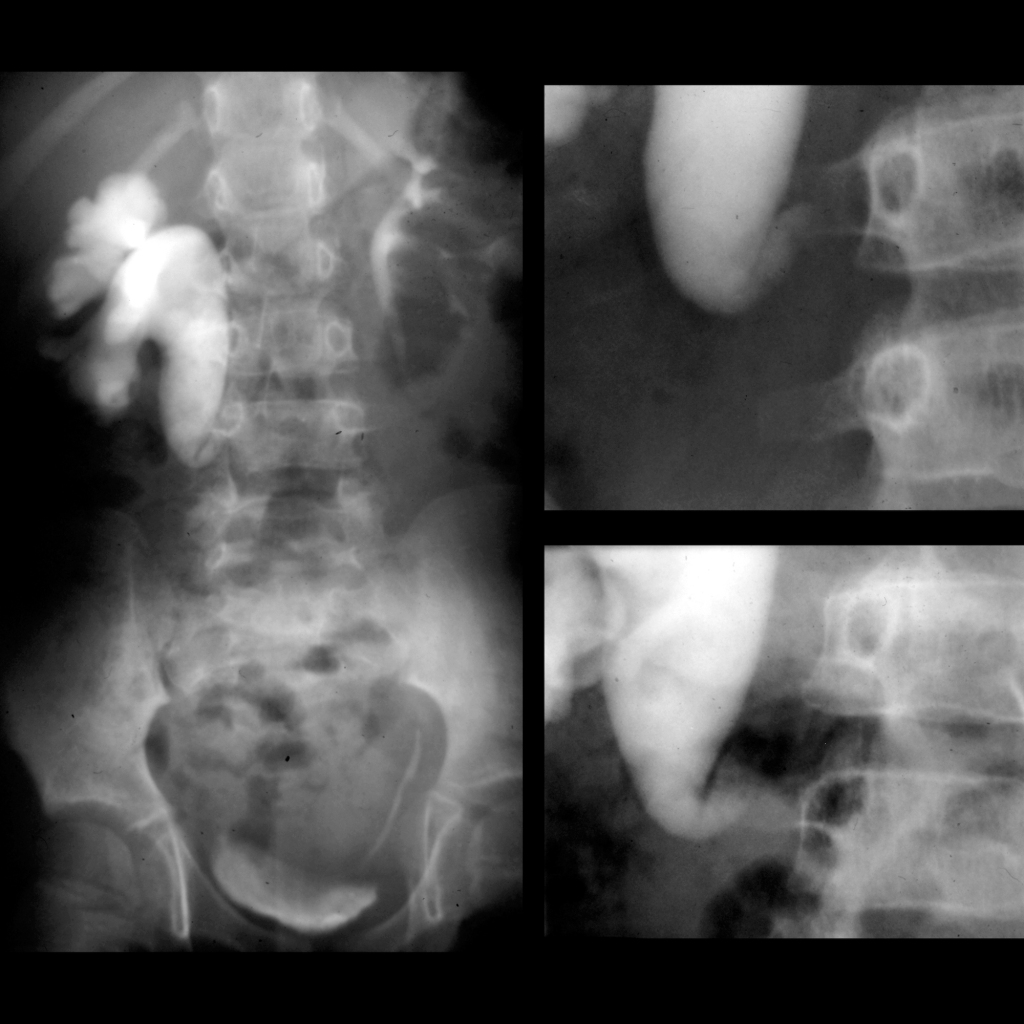
The diagnosis was retrocaval ureter causing right ureteropelvic junction obstruction.
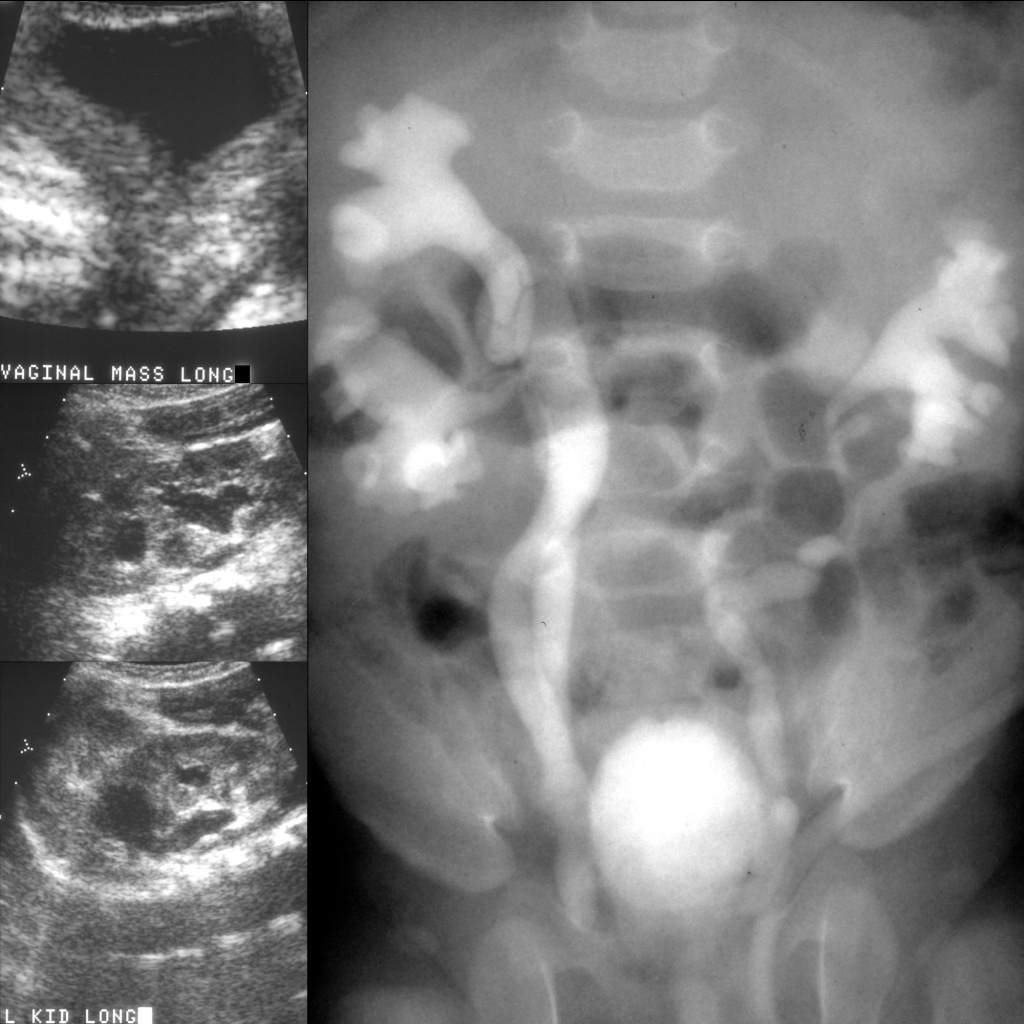
The diagnosis was prolapsed ectopic ureterocele from the upper pole of the left kidney in a patient with bilateral duplicated kidneys.
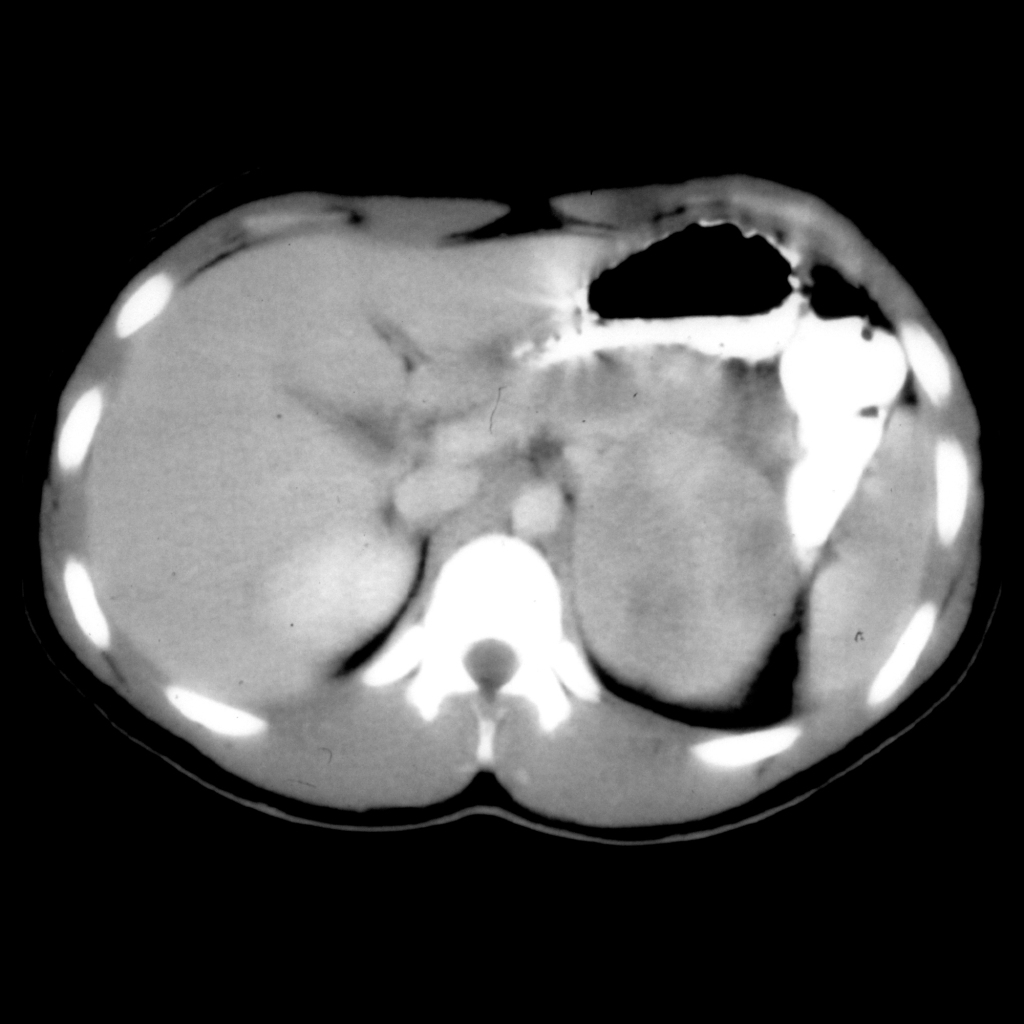
The diagnosis was adrenocortical carcinoma.
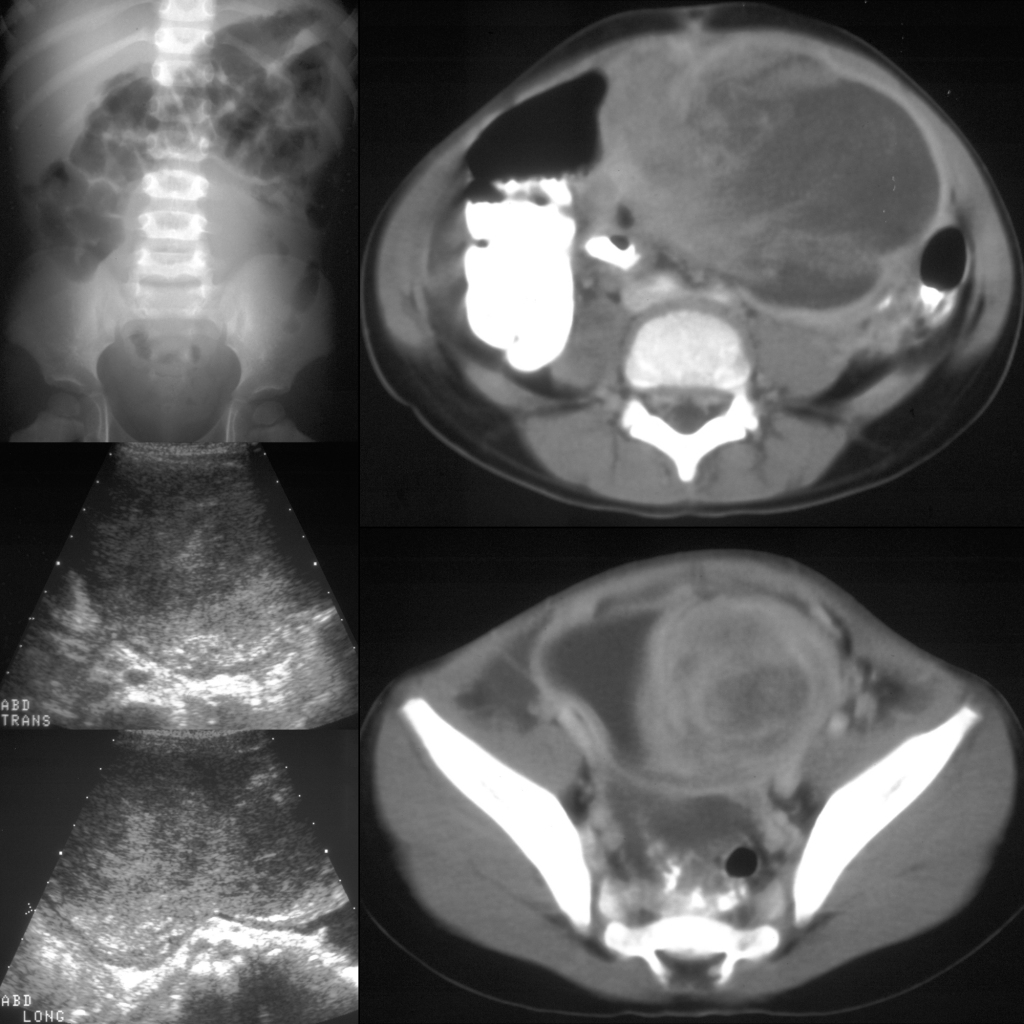
The diagnosis was rhabdomyosarcoma arising from the dome of the bladder.
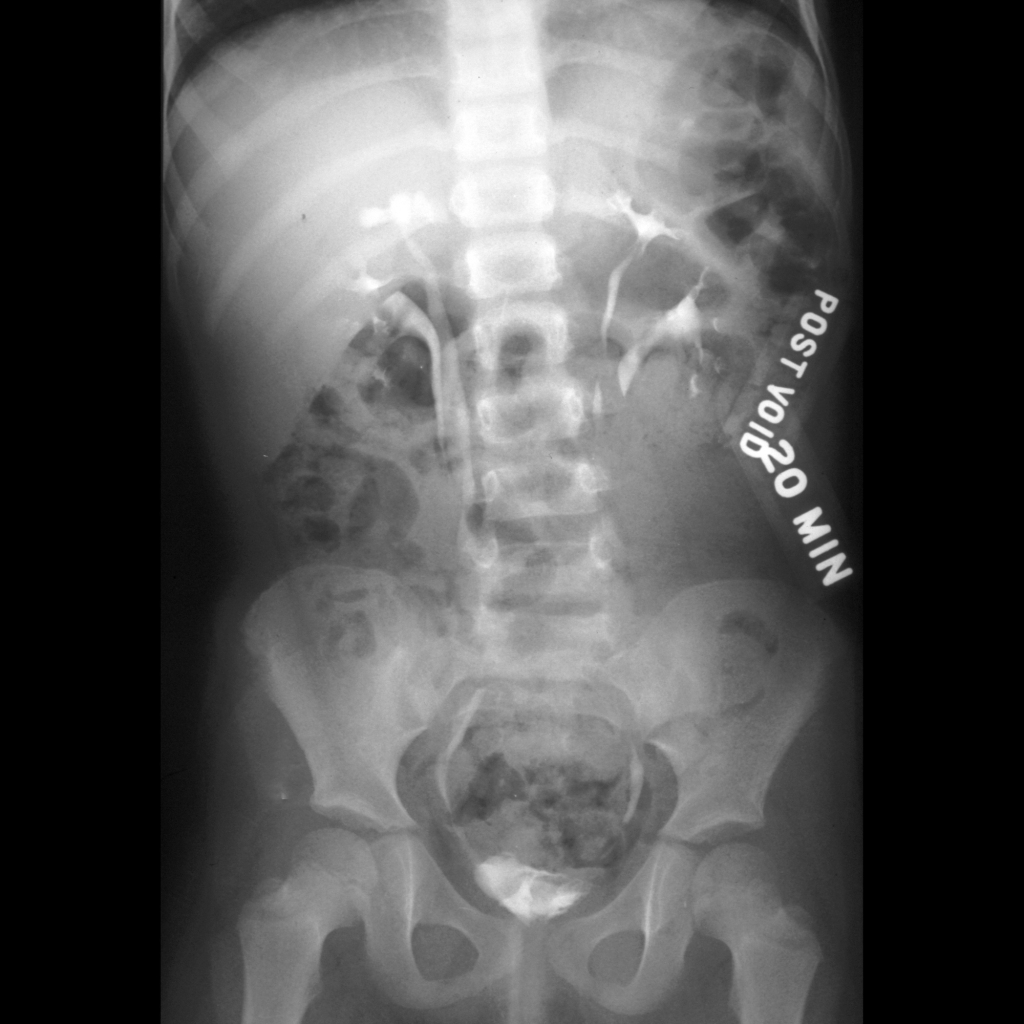
The diagnosis was bilateral duplicated kidneys with bilateral ectopic ureteroceles.
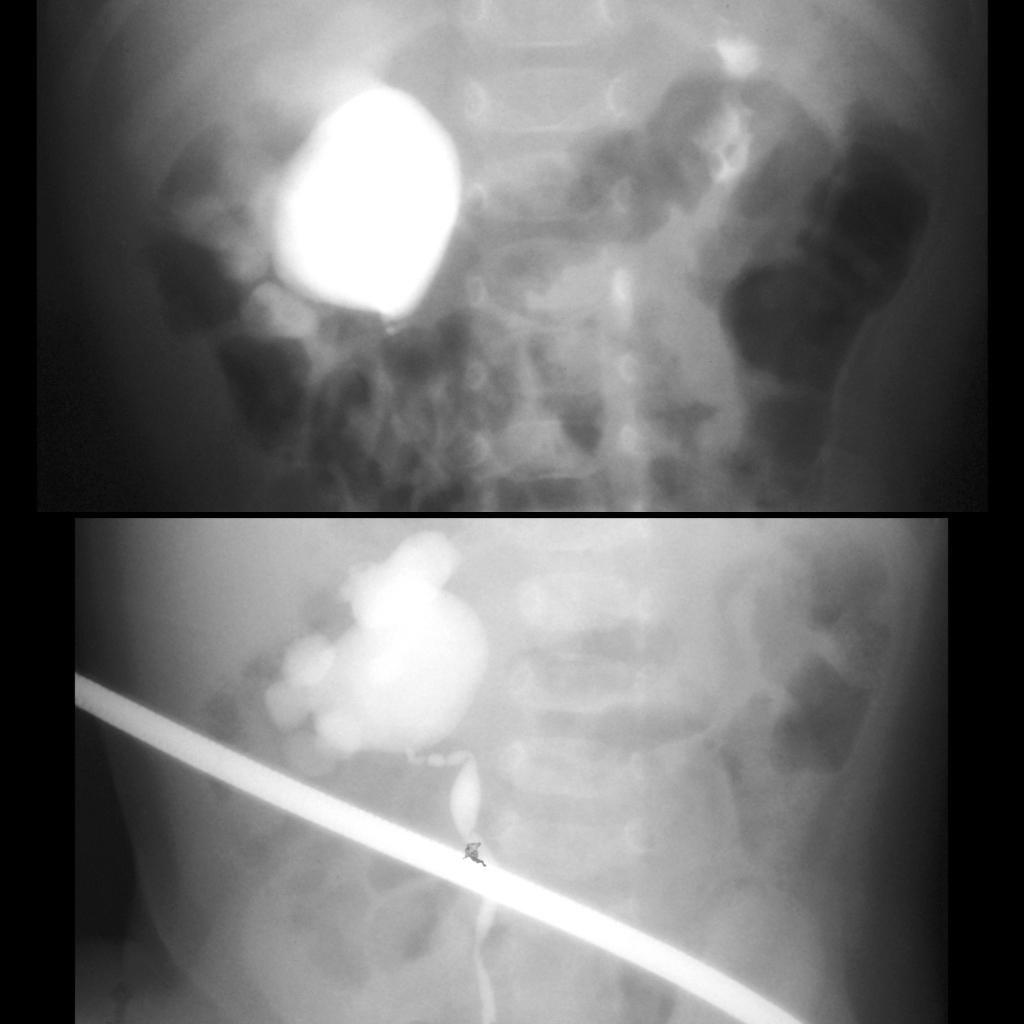
The diagnosis was right ureteropelvic junction obstruction due to a crossing vessel.
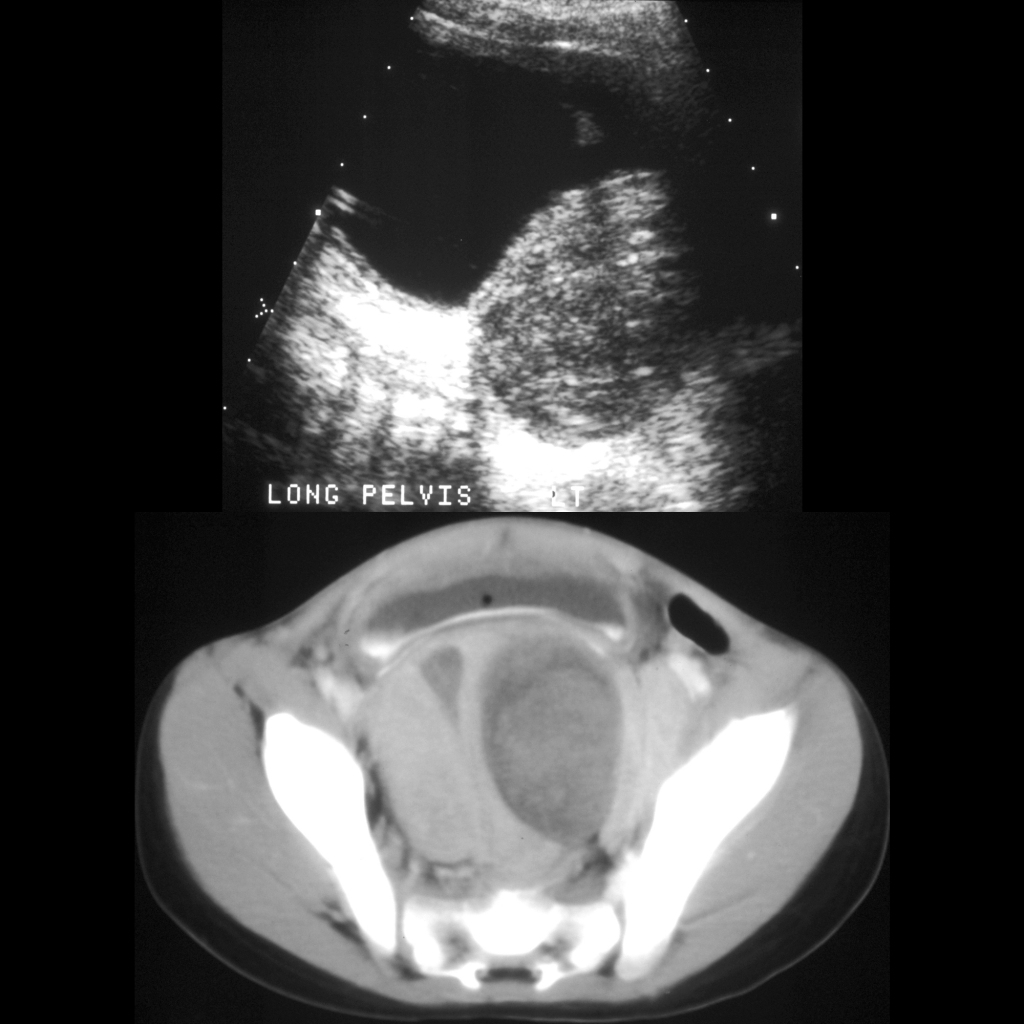
The diagnosis was rhabdomyosarcoma of the prostate.