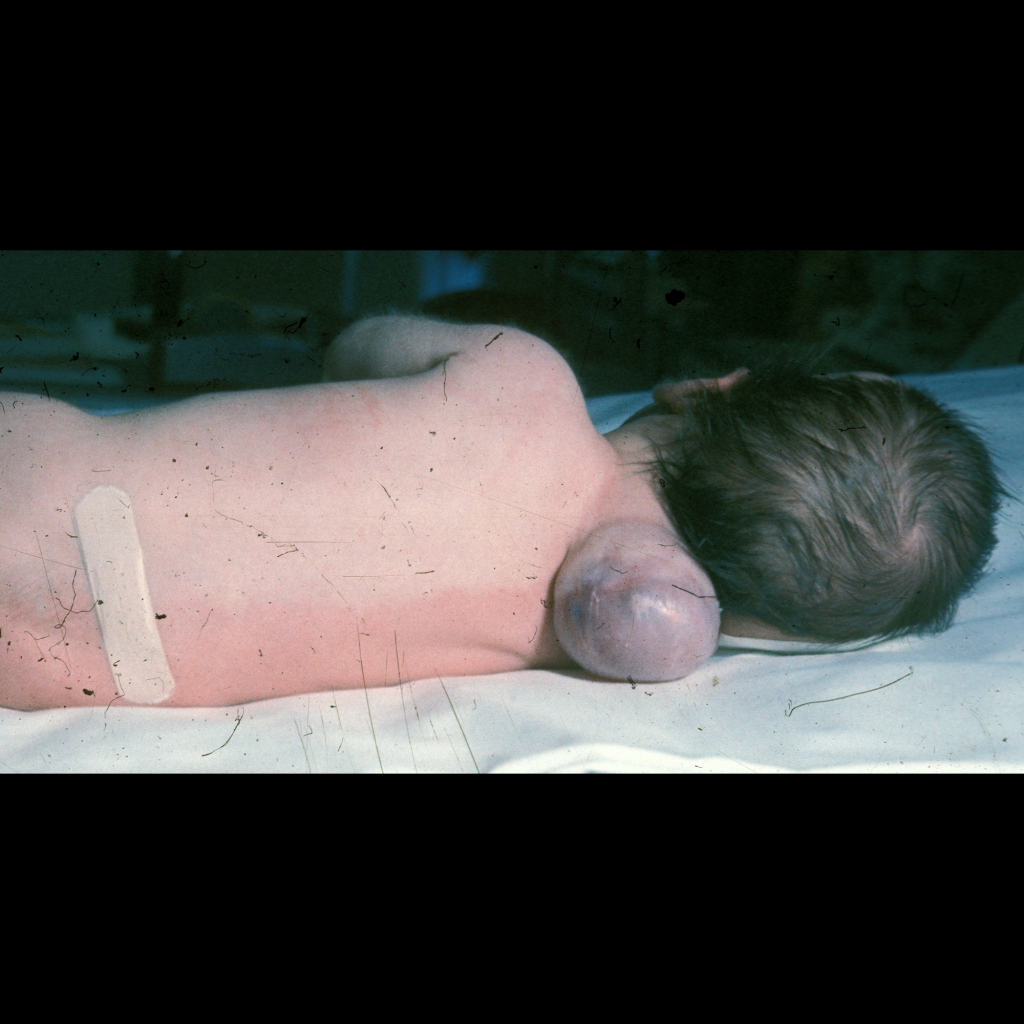
The diagnosis was occipital myelomeningocele.

The diagnosis was occipital myelomeningocele.
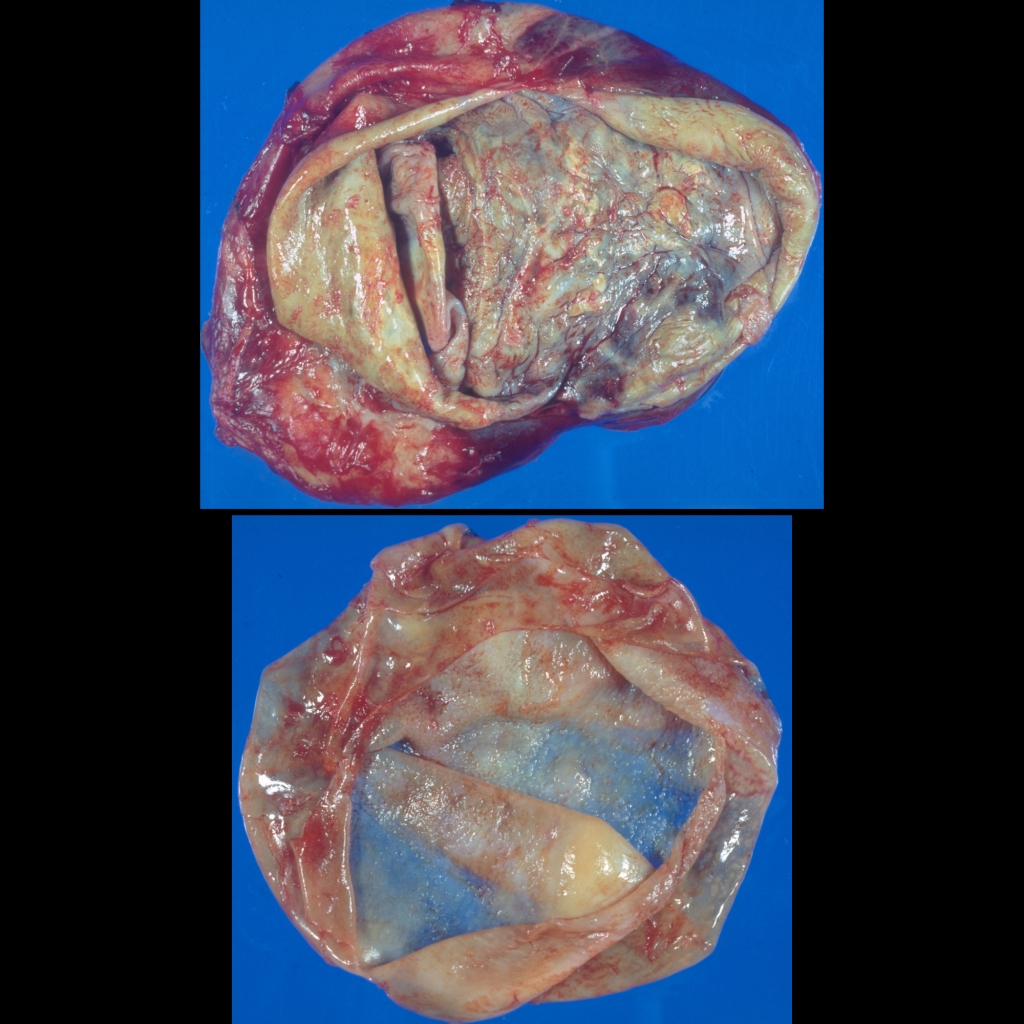
The diagnosis was hydatid disease.
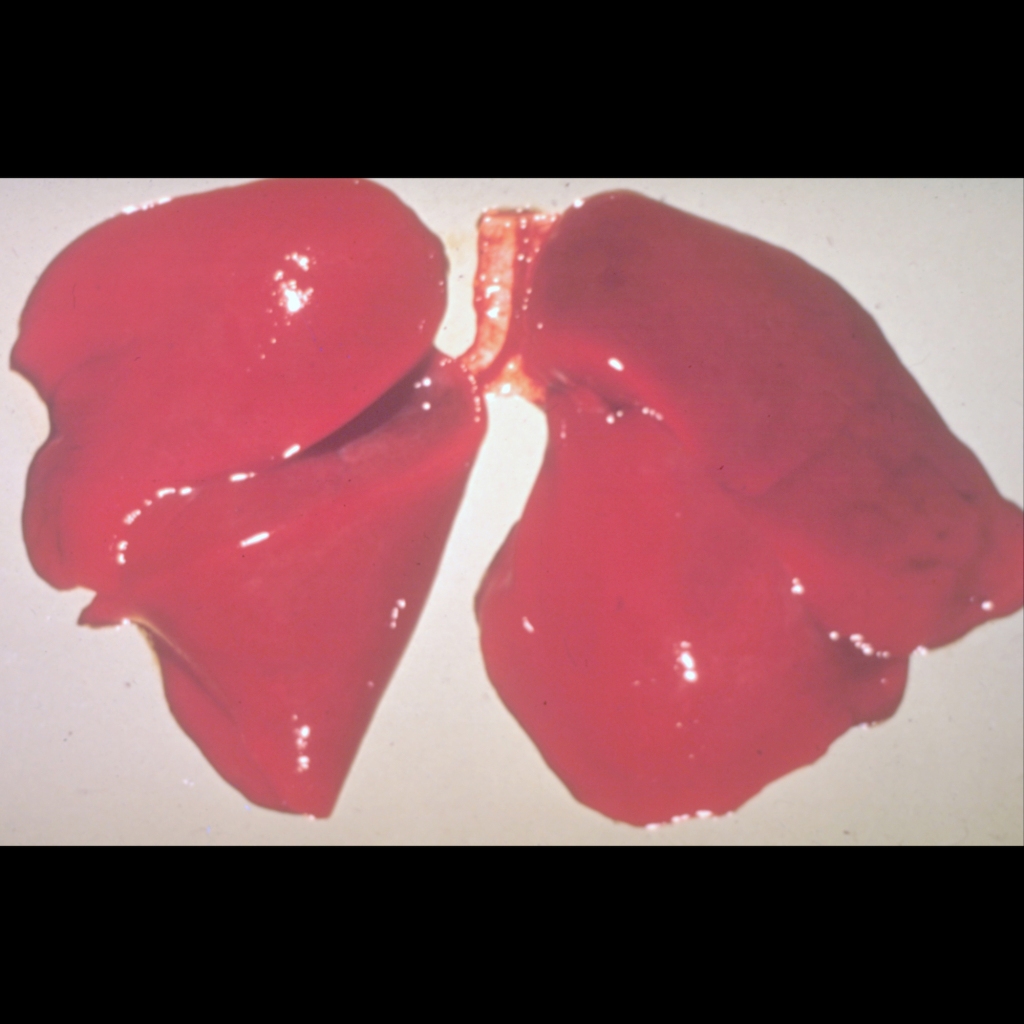
The diagnosis was respiratory distress syndrome.
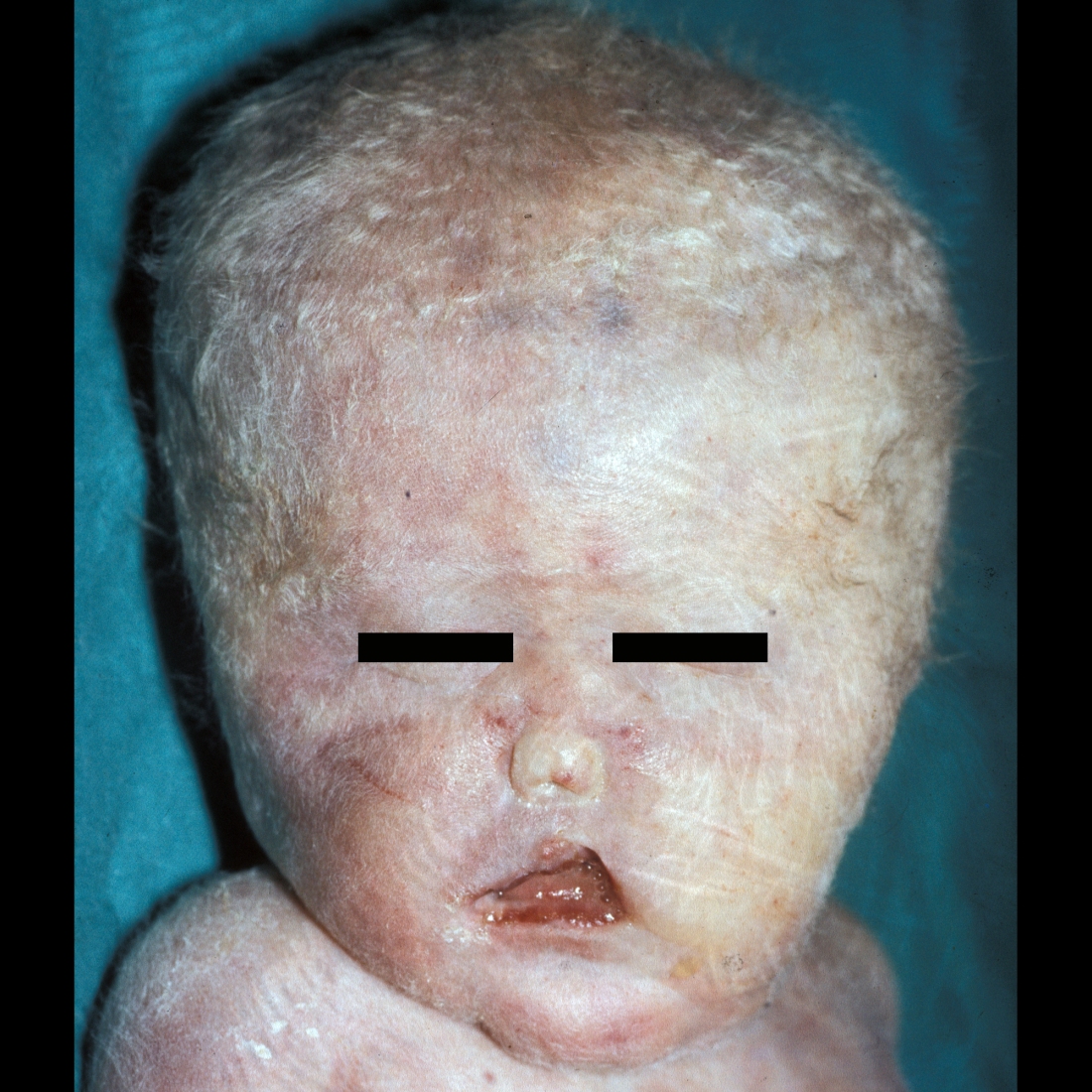
The diagnosis was alobar holoprosencephaly.
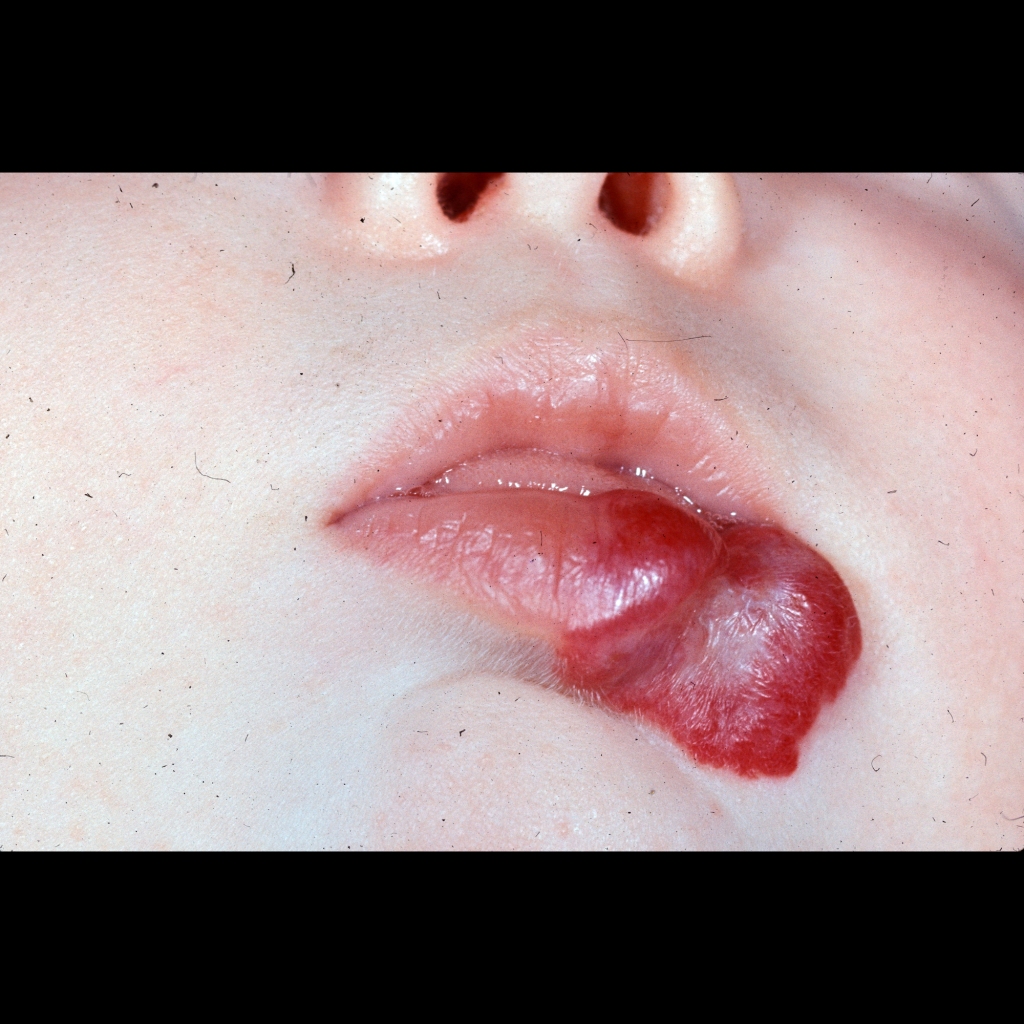
The diagnosis was soft tissue hemangioma.
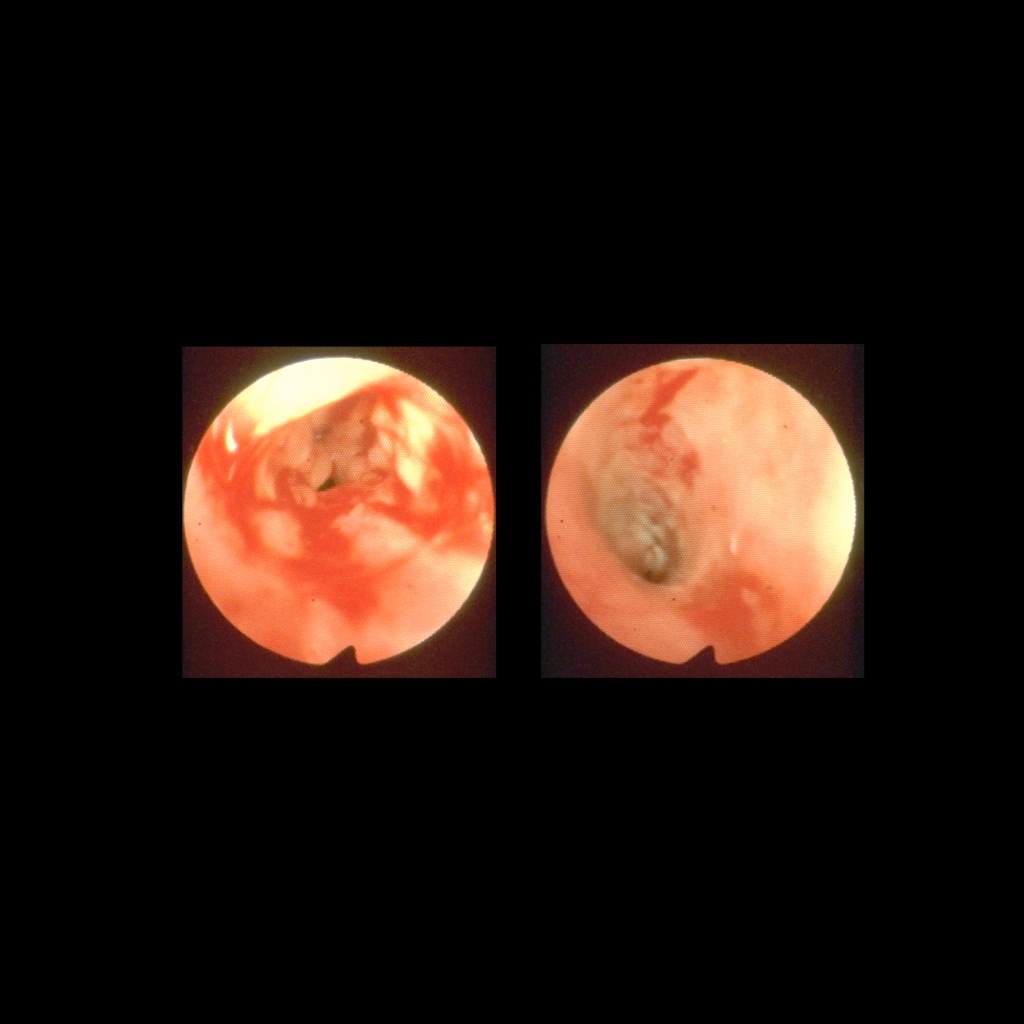
The diagnosis was esophagitis due to gastroesophageal reflux.
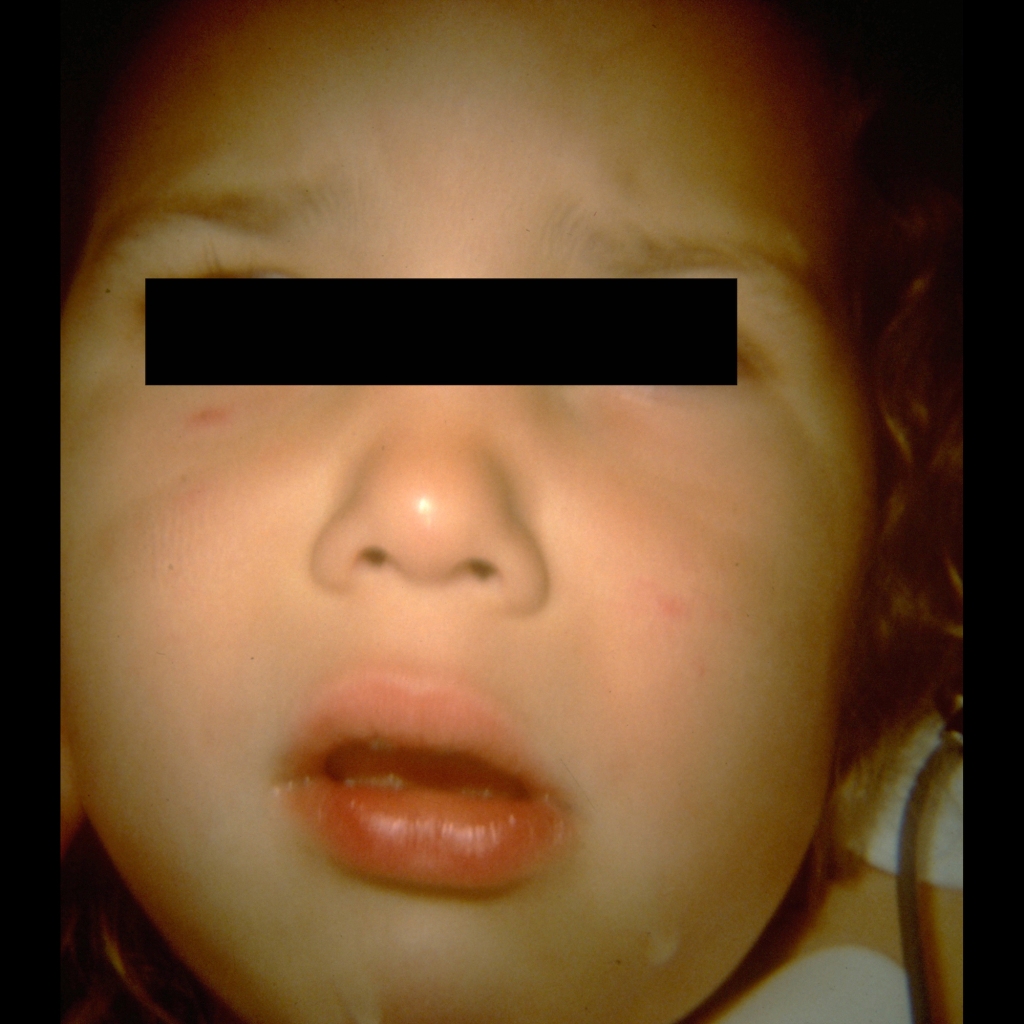
The diagnosis was epiglottitis.
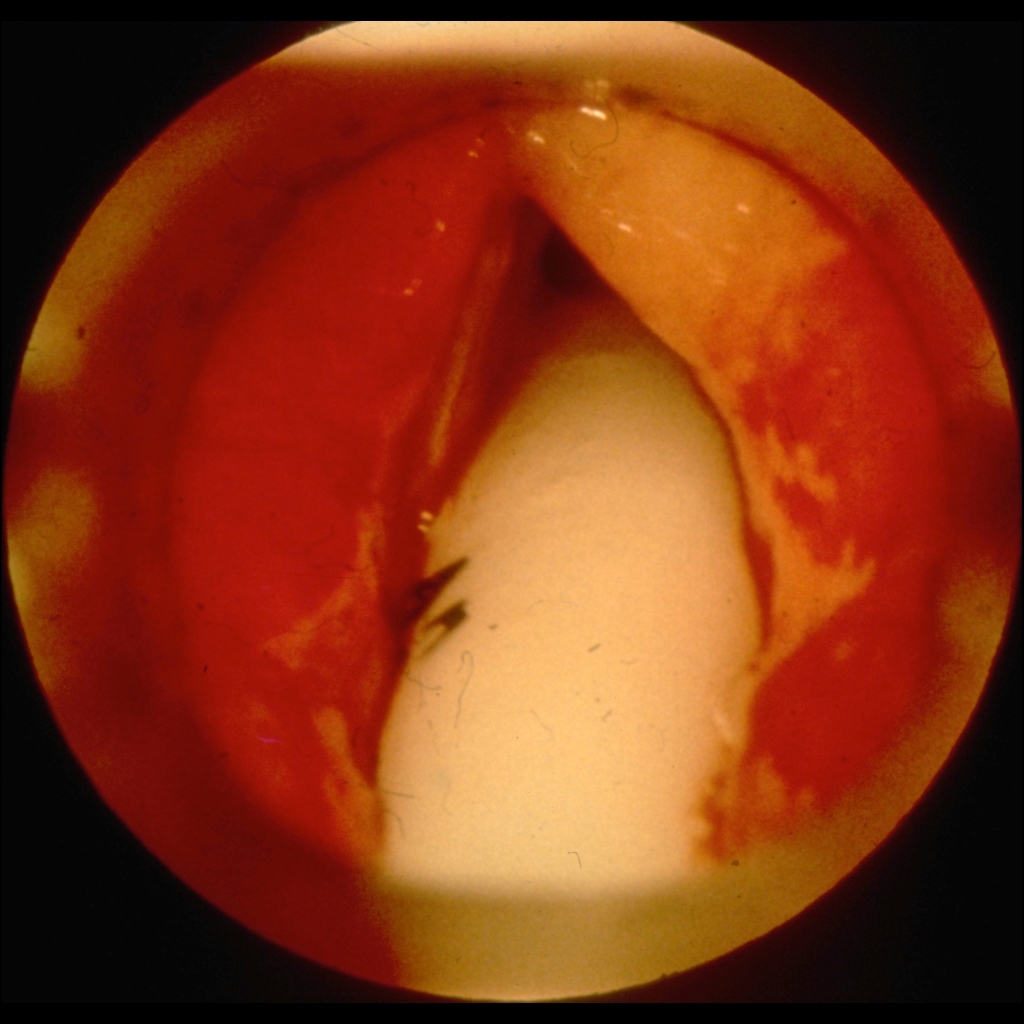
The diagnosis was epiglottitis.
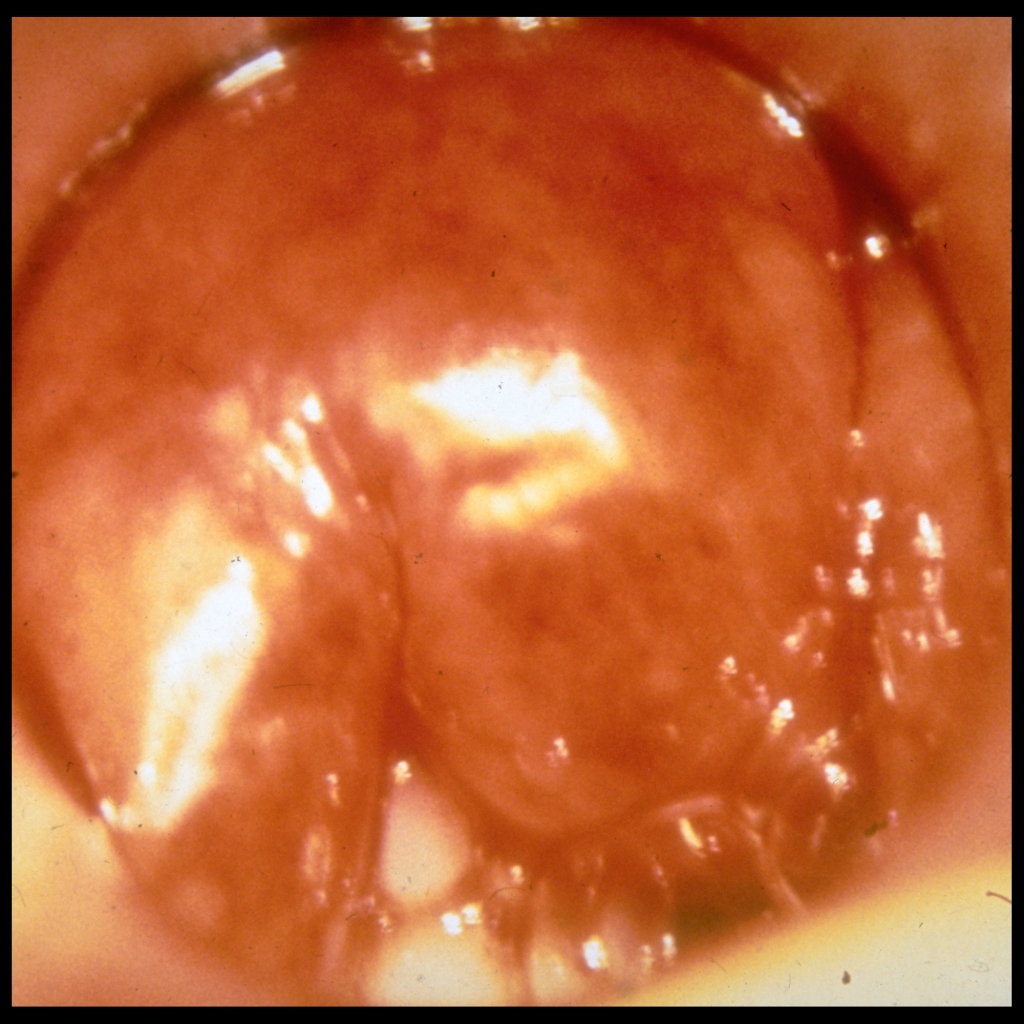
The diagnosis was epiglottitis.
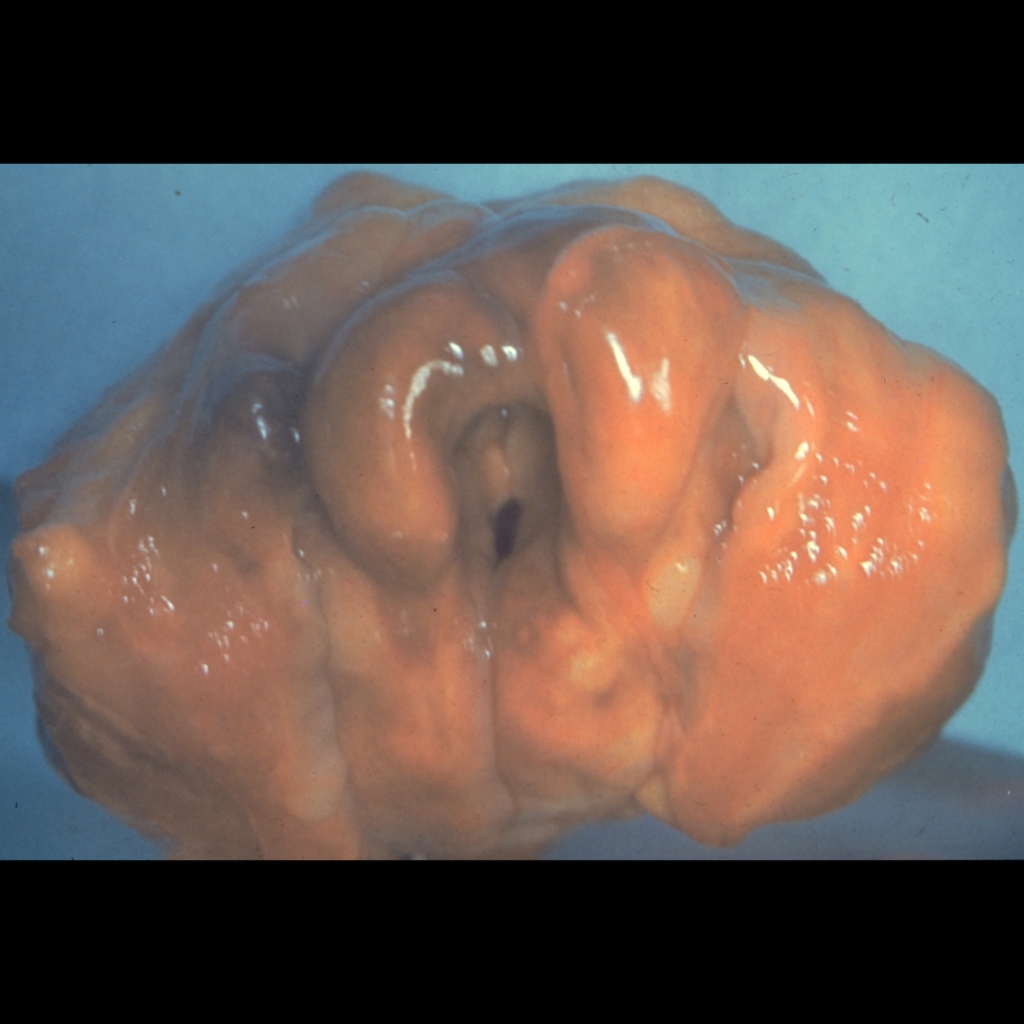
The diagnosis was epiglottitis.

The diagnosis was main pulmonary arterial aneurysm due to absent pulmonary valve syndrome.

View the illustrated DDX of esophageal pH probe malfunction.

View the illustrated DDX of esophageal pH probe malfunction.

The diagnosis was arrested pneumatization of the skull base.

The diagnosis was delayed skeletal maturation due to congenital hypothyroidism.

The diagnosis was a simple renal cyst and not a calyceal diverticulum.

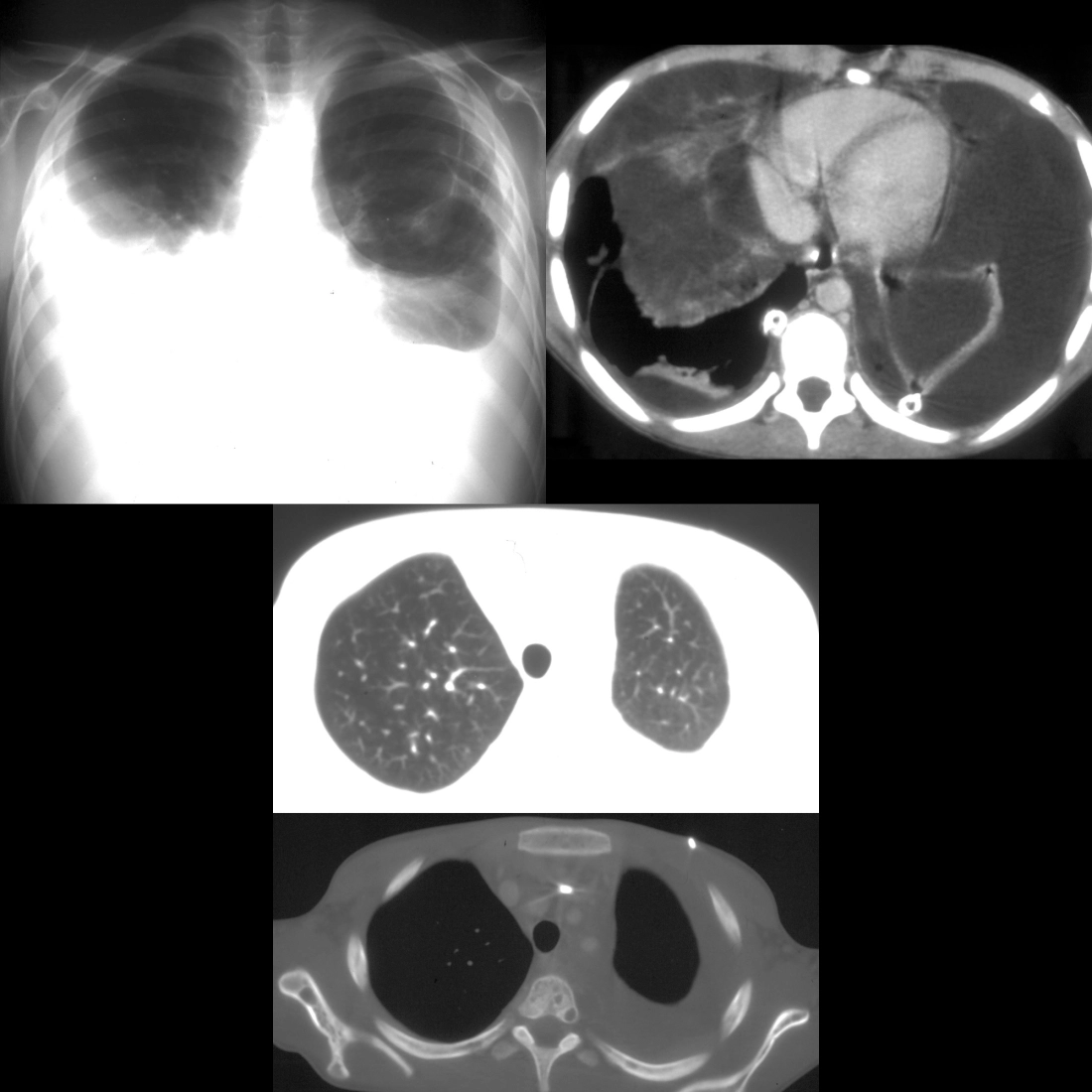
The diagnosis was lymphangioleiomyomatosis with bilateral chylous effusions.
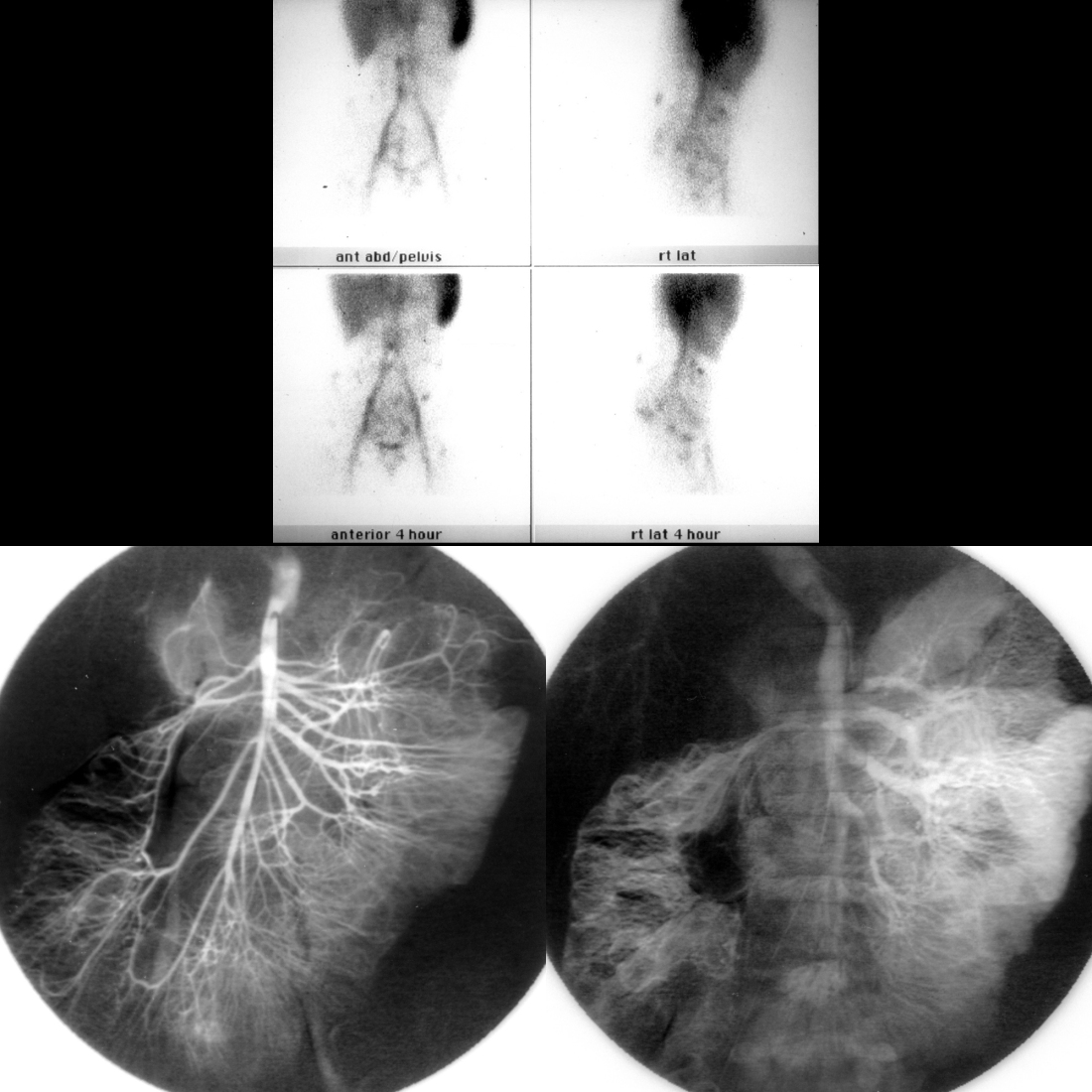
The diagnosis was blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome.

View the illustrated DDX of cardiac pacemaker lead malfunction.

View the illustrated DDX of cardiac pacemaker lead malfunction.
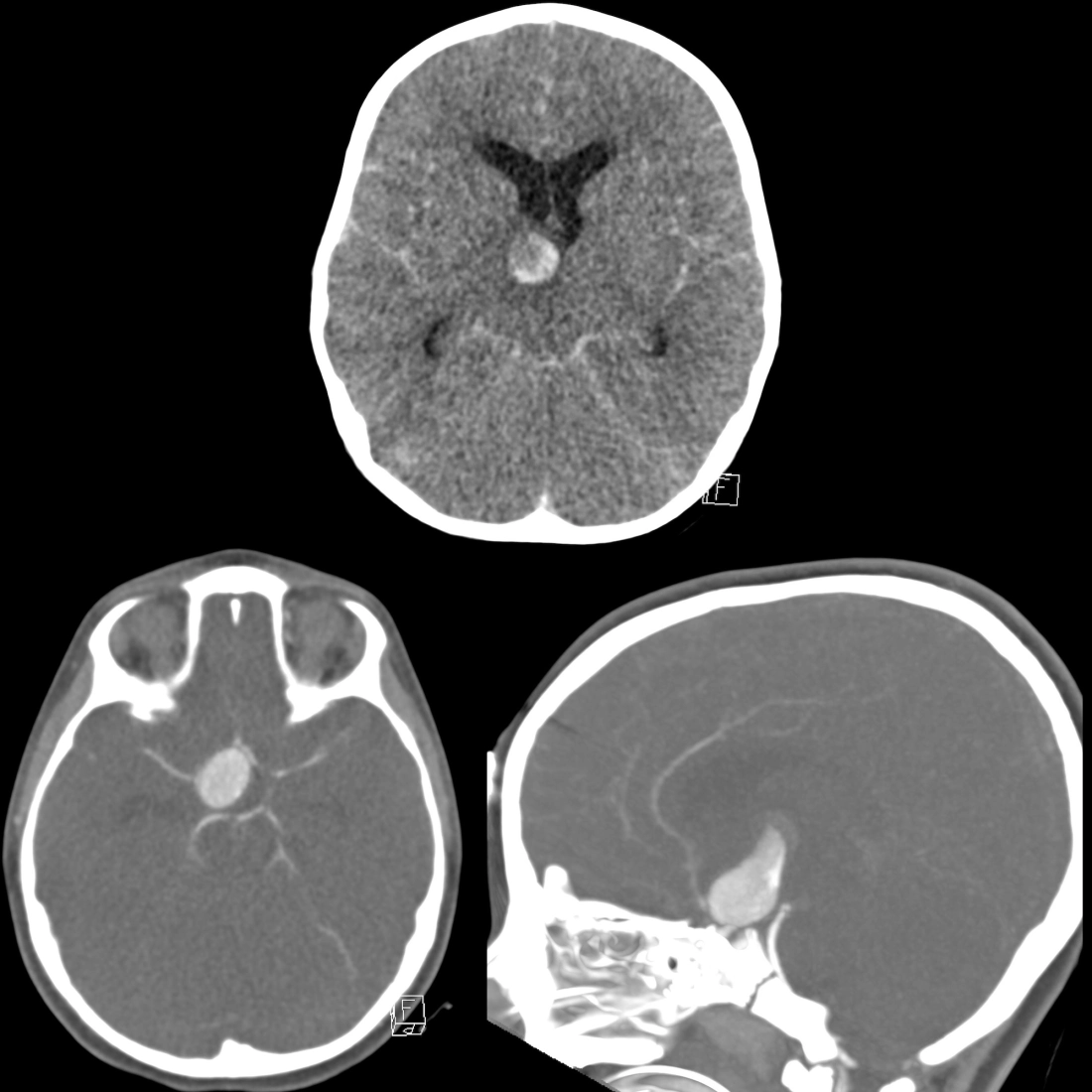
The diagnosis was giant intracranial aneurysm which had ruptured causing subarachnoid hemorrhage and diffuse cerebral edema.
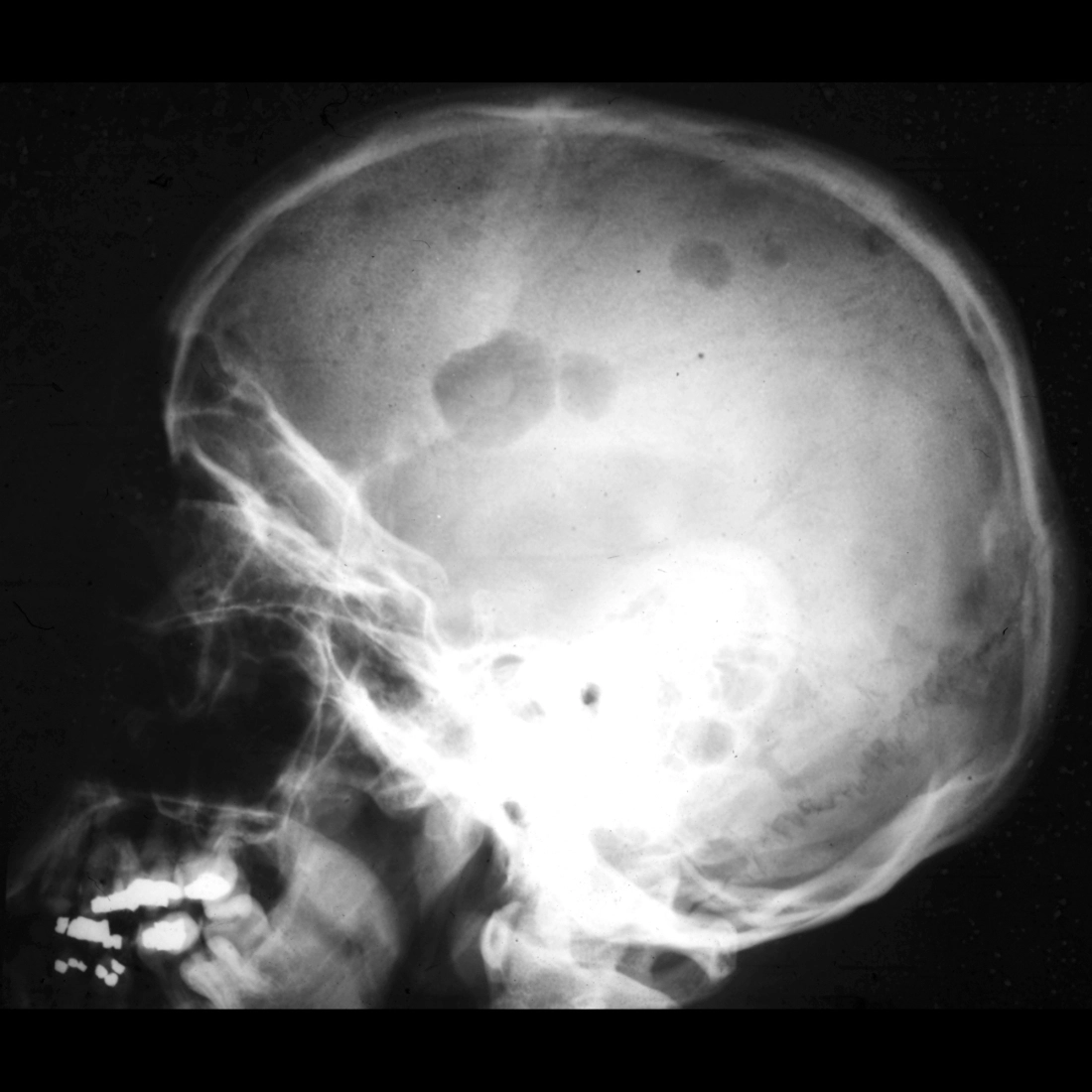
The diagnosis was multiple myeloma.
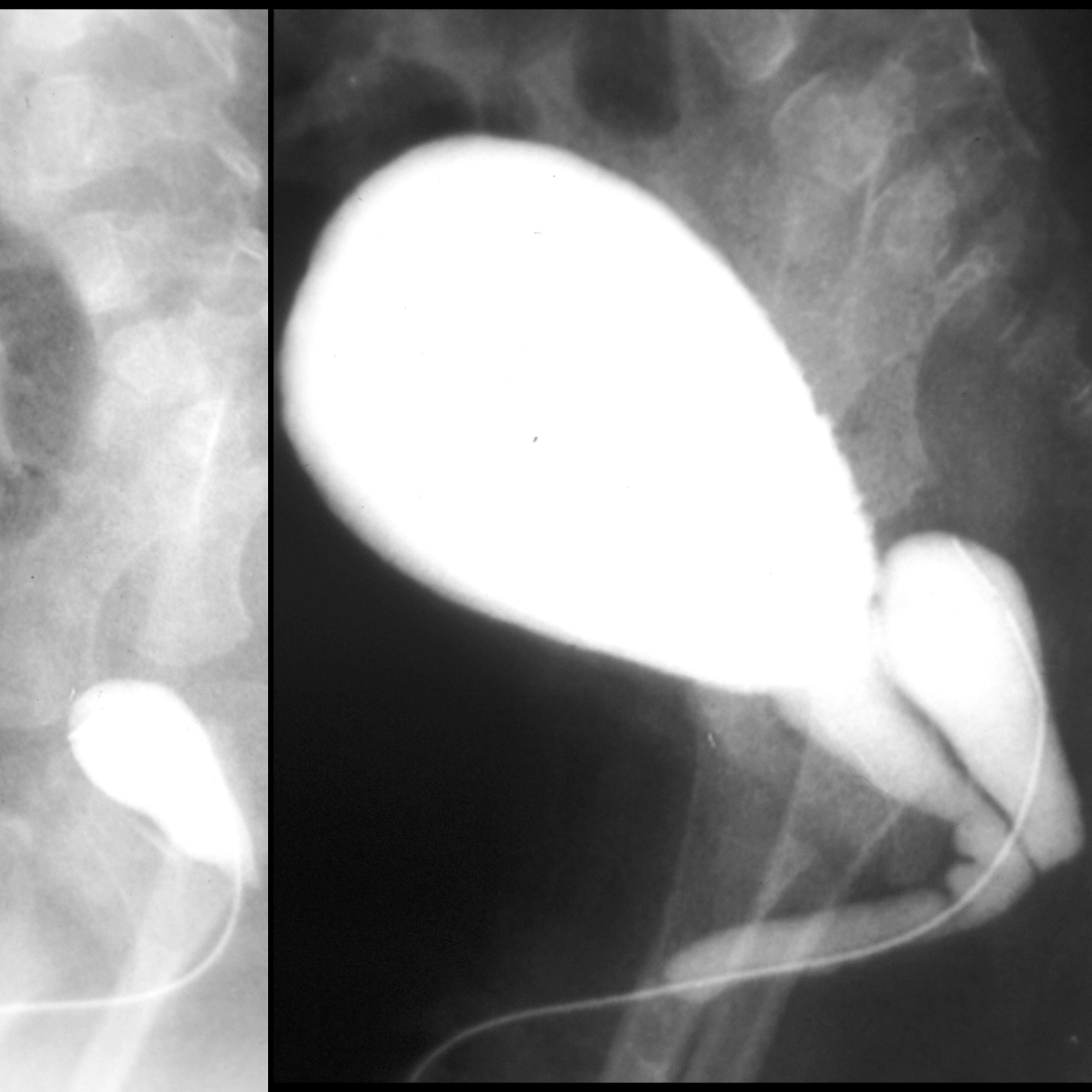
The diagnosis was prostatic utricle cyst.
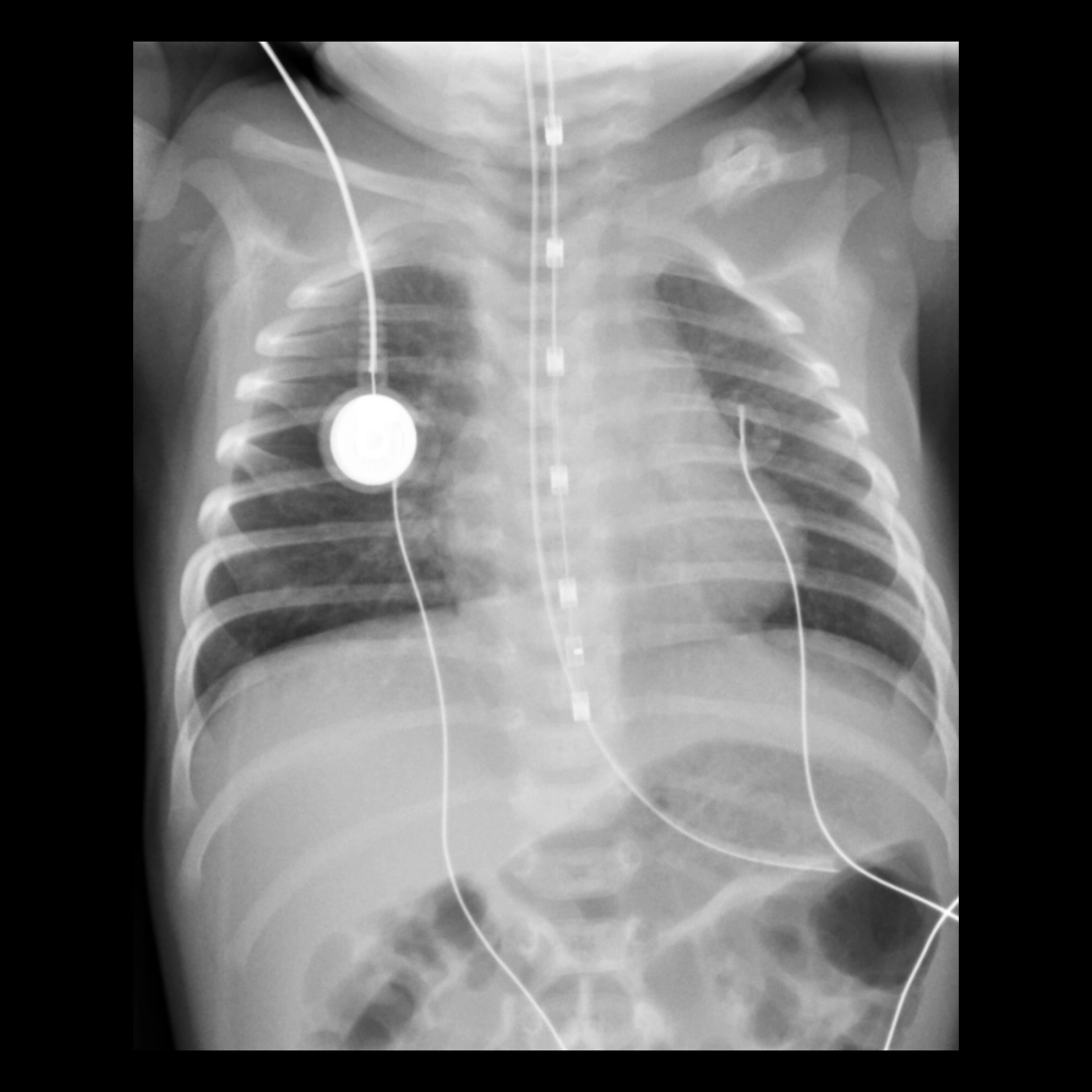
The diagnosis was correct position of the esophageal pH probe sensor / measurement lead.